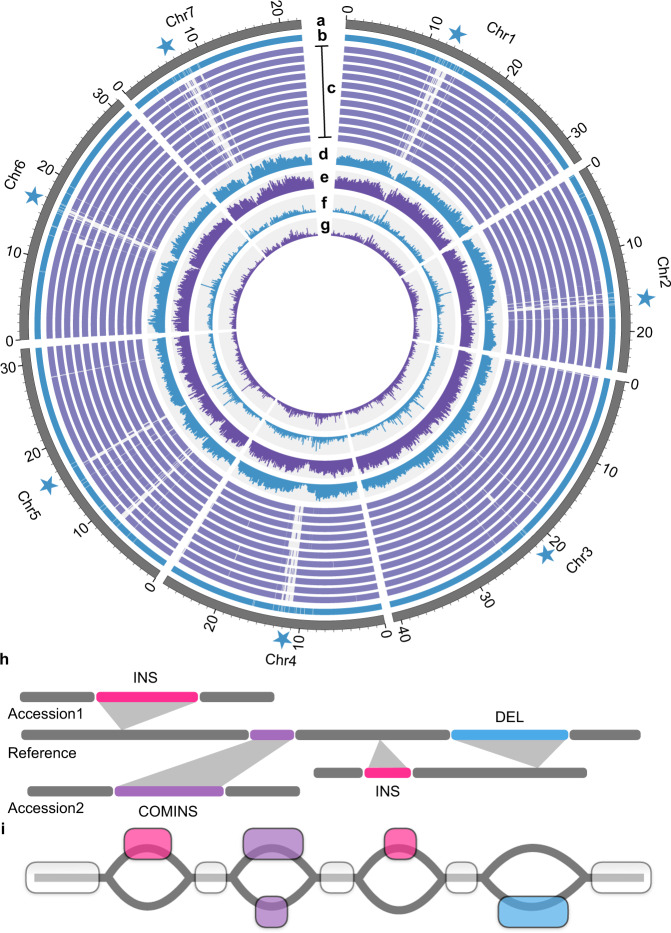
Fig. 3. Collinear alignment blocks, genetic variants, and graph-based pan-genome of cucumber.
a Pseudo-chromosomes of the 9930 reference. Pentagrams mark approximate positions of centromeres. b Contig tracks of the 9930 reference. Gaps are shown by white bars. c Collinear alignment blocks of genomes of XTMC, Cu2, Cuc37, Gy14, 9110gt, Cuc80, Cuc64, W4, W8, Hx14, Hx117 (from upper to lower) to the 9930 reference. White bars represent non-synteny regions. d, e Variant density histograms of SNPs (d) and small InDels (e) (number/200 kb; 0–5000 for SNPs and 0–2000 for small InDels). f, g Distribution histograms of large insertions (f) and deletions (g) (number/200 kb; 0–120 for large insertions and deletions). h Schematic illustration of SVs from genomes of two example accessions and the linear reference genome sequences used to construct the graph-based pan-genome. Colored bars represent SV sequences and gray bars denote reference-type fragments. INS insertion, DEL deletion, COMINS complex insertion. i Cucumber graph-based pan-genome that integrates sequences and positions of SVs while preserves the linear reference coordinates. Transparent blocks illustrate sequences conserved among genomes of the 11 accessions and the reference, while colored blocks show fragments with SVs compared to the reference genome. Gray lines denote possible paths within the graph.