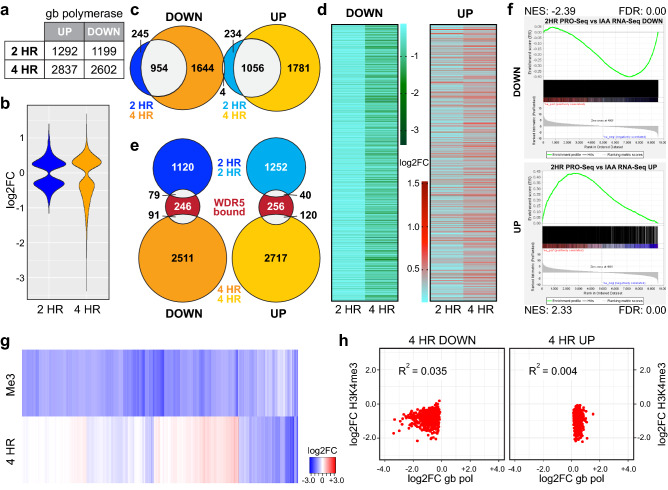
Figure 4.
Rapid impact of WDR5 loss on transcription. (a) Summary of PRO-Seq from AIDW cells treated with 100 μM IAA for 2 or 4 h. Table shows the number of genes that had a significant increase or decrease in gene body (gb)-associated RNA polymerases at the 2 and 4 h timepoints (FDR < 0.05). N = 3. (b) Violin plot, displaying the magnitude of all significant transcription changes associated with 2 or 4 h of IAA treatment, plotted as log2FC. (c) Venn diagram, showing overlap of genes in the 2 and 4 h IAA treatment sets with significant changes in gb-associated polymerases, according to whether gb-polymerase density decreased (DOWN) or increased (UP) with IAA treatment. (d) Heatmaps, showing log2FC values for genes with decreased or increased gb-associated polymerases in the 2 and 4 h IAA treatments. (e) Venn diagram, showing the overlap of genes with significant changes in gb-associated polymerases with those bound by WDR5 in Ramos cells4, broken down according to whether gb-polymerase density decreased (DOWN) or increased (UP) with IAA treatment. (f) GSEA showing the enrichment of genes with significant decreases (top) or increases (bottom) in transcript changes detected in IAA RNA-Seq against gb-associated polymerases following 2 h of IAA treatment (PRO-Seq). NES normalized enrichment score, FDR false discovery rate. (g) Heatmap, showing log2FC values for genes changed in either gb-associated polymerases in 4 h IAA treatments (PRO-Seq) or H3K4me3 (me3) levels in IAA-treated cells. (h) Scatter plots, comparing log2FC in H3K4me3 induced by WDR5 degradation with log2FC in gb-associated polymerases induced by WDR5 degradation after 4 h (4 HR) of IAA treatment. The plot on the left shows genes with decreased polymerase density; the plot on the right shows genes with increased polymerase density. The coefficient of determination (R2) is shown.