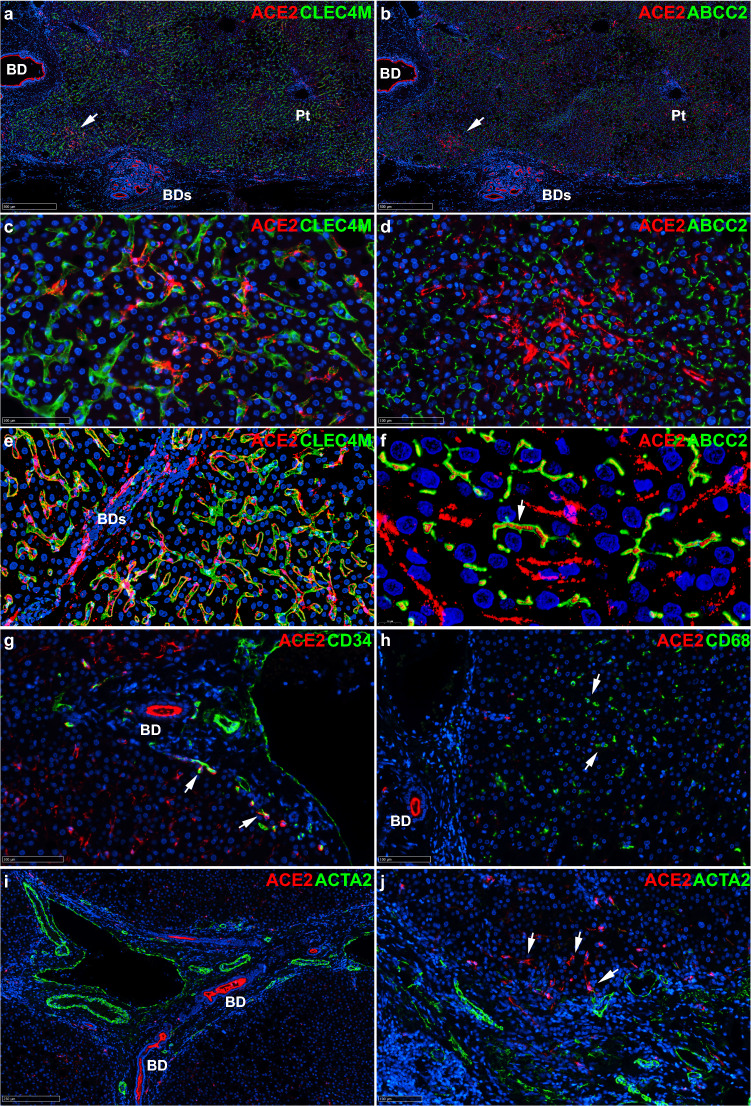
Figure 3.
ACE2 is detected in sinusoidal endothelial cells, bile ducts and capillaries of the periportal plexus in non-tumor livers. Co-immunostaining for ACE2 and the indicated markers in three non-tumor livers from patients undergoing resection of colon cancer metastasis. Representative images are shown. ACE2 appears in red by immunofluorescence, other markers in green and nuclei in blue (DAPI staining). (a), (b) Low power views (X5 magnification) show ACE2 in a bile duct (BD) and in a zone with mild inflammatory infiltration (arrow) and dystrophic bile ducts (BDs). The sinusoidal endothelial cell marker CLEC4M (a.k.a. DC-SIGNR) and the bile canaliculi marker ABCC2 (a.k.a. MRP2) show lobular staining at this magnification. Pt, portal tract. (c), (d) At X30 magnification, ACE is detected in sinusoidal endothelial cells, which can be identified by comparing CLEC4M (c) and ABCC2 (d) staining. Digital images were acquired with a microscope scanner and a X40 objective and exported at the indicated magnifications (Nanozoomer, Hamamatsu Photonics). (e), (f) Confocal scans of whole tissue sections as Z-stacks of 4 X 500 nm focusing steps at X40 (e) and X143 (f). ACE2 is detected in CLEC4M-positive sinusoidal endothelial cells (e) and within ABCC2-positive bile canaliculi (f). ACE2-positive bile ducts (BDs) are seen in (e). (g) At 28X magnification, ACE2 is sparsely detected in CD34-positive endothelial cells of the periportal vascular plexus (arrows). (h) At 24X magnification, no evidence of ACE2 detection in CD68-positive Kupffer cells. (i), (j) No evidence of ACE2 detection in vascular smooth muscle (i, 10X magnification) or in ACTA2 (a.k.a alpha smooth muscle actin)-positive cells within portal tract stroma (j, 20X magnification). ACE2-positive cells within the portal tract are ACTA2 negative (arrows).