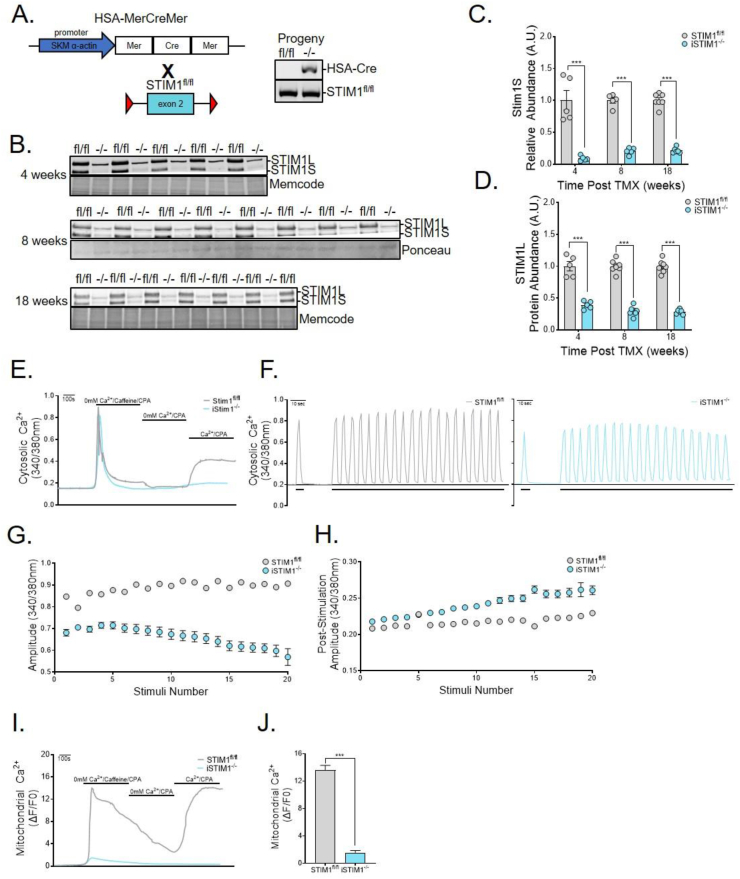
Figure 2.
Conditional deletion of STIM1 in adult muscle abolishes SOCE. (A) Schematic depicting the breeding strategy to generate mice with inducible muscle-specific deletion of STIM1. Transgenic HSA-MerCreMer mice were crossed with mice in which exon 2 of the STIM1 gene is flanked by loxP sequences (STIM1fl/fl). Adult mice received tamoxifen (TMX) at ages of 12–13 weeks (B–D) or 8 weeks (E–J). TMX-treated transgenic HSA-MerCreMer:STIM1fl/fl are denoted as iSTIM1−/− throughout the manuscript. (B) Western blots and quantification of (C) STIM1S and (D) STIM1L abundance normalized to total protein in gastrocnemius muscles 4, 8, and 18 weeks after TMX (n = 5–8). (E) Representative traces of cytosolic Ca2+ in response to a standard SOCE protocol in FDB fibers loaded with Fura-2 (n = 4). (F) Representative traces of cytosolic Ca2+ transients generated with a single (2 s pulse [short bars]) or repeated bursts (2 s pulse at 50 HZ every 5 s [long bar]) of electrical activity in STIM1fl/f (left) and iSTIM1−/− (right) FDB myofibers loaded with Fura-4 (n = 4). The amplitude of cytosolic Ca2+ in Fura-4 loaded FDB fibers (G) during and (H) after each electrical stimulus (2 s at 50 HZ) (n = 17–23 fibers). (I) Representative traces and (J) quantification of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake in response to a standard SOCE protocol in FDB fibers loaded with Rhod-2 (n = 12–13). Data in (C, D, and J) were analyzed using Student's two-tailed t-test. n represents biological replicates.