FIGURE 3.
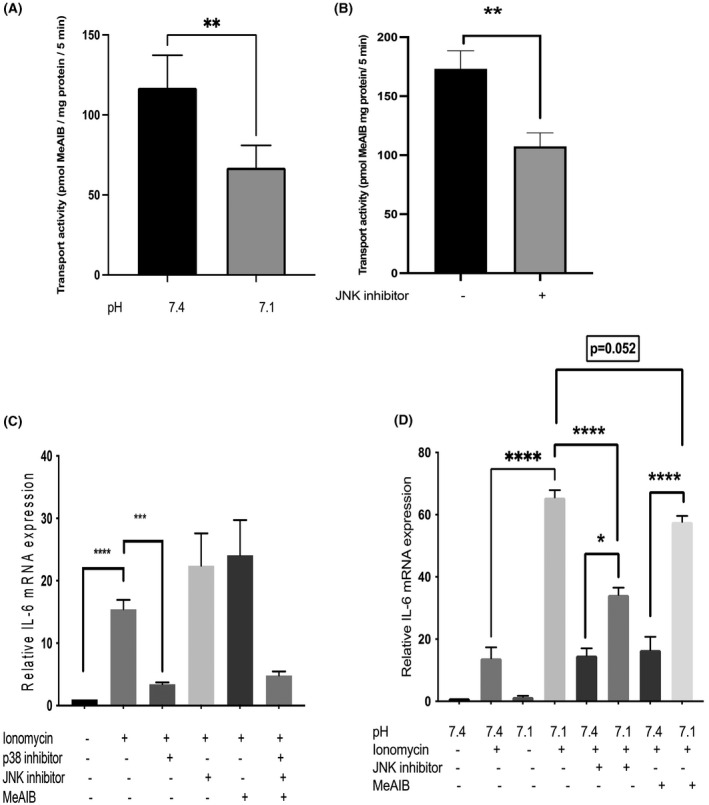
Effect of low extracellular pH and inhibition of JNK and of SNAT2(SLC38A2) amino acid transporters on interleukin‐6 mRNA in L6‐G8C5 myotubes. (A) Acute effect of low extracellular pH (applied only during the transport assay) on SNAT2(SLC38A2) transporter activity in L6‐G8C5 myotubes. 14C‐MeAIB transport was assayed in 5 min incubations in HBS medium at pH 7.1 or 7.4. Pooled data are shown from six independent experiments, with five replicate culture wells in each experiment. **p < 0.01 versus pH 7.4 control. (B) Cells were pre‐incubated for 4 h at pH 7.4 in MEM/2% DFBS with JNK MAPK inhibitor SP600125 (10 µM) or in control cultures without inhibitor. The 14C‐MeAIB transport rate was then immediately assayed as in (A) but at pH 7.4 only and in the absence of the inhibitor. Pooled data are shown from n = 3 independent experiments, with five replicate culture wells in each experiment. **Denotes significant difference from Control p < 0.01. (C) Myotubes were cultured for 6 h in MEM medium at pH 7.4 with 2 mM l‐glutamine and 2% dialysed foetal bovine serum, either with no drugs as a baseline control or with 0.5 µM ionomycin with and without drugs. The drugs tested were 10 µM JNK inhibitor (SP600125) and 10 mM MeAIB. Pooled data are shown from n = 3 independent experiments. Significant differences between conditions are shown as ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (D) IL‐6 mRNA was measured after 6‐h incubations as in (C) but the pH of the MEM medium was either a control pH of 7.4 or an acidic pH of 7.1. Pooled data are shown from n = 3 independent experiments. Significant differences between conditions are shown as *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001
