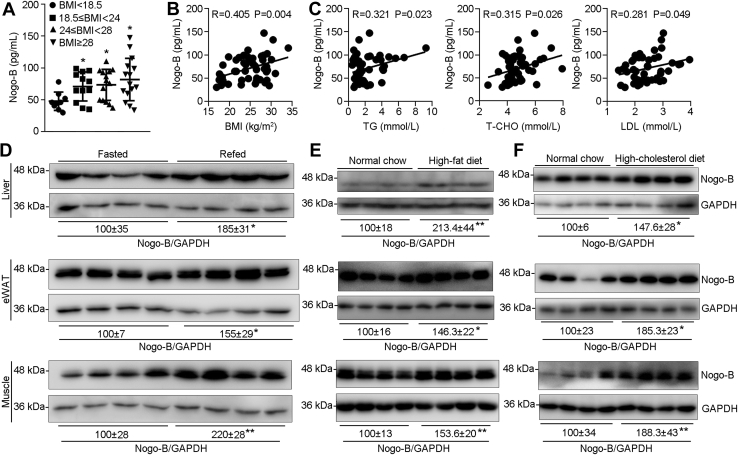
Figure 1.
Activated Nogo-B is associated with obesity and overnutrition conditions. Serum samples collected from volunteers (n = 50) were determined levels of Nogo-B, TG, T-CHO, and LDL. A, Nogo-B levels were grouped based on the BMI ranges (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2, n = 9; 18.5 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 24 kg/m2, n = 12; 24 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 28 kg/m2, n = 14; BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2, n = 15). The correlation coefficient between Nogo-B and BMI (B) or lipid profiles (TG, T-CHO, and LDL) (C) in humans was analyzed using the Pearson correlation test with 95% confidence interval. Male C57BL/6J mice (∼7 weeks old) were used to conduct fasting (D), 1 week HFD (E), or high-cholesterol diet (F) feeding, followed by determination of Nogo-B expression by Western blot with total proteins extracted from liver, eWAT, and skeletal muscle samples. ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 (n = 4). BMI, body mass index; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; HFD, high-fat diet; LDL, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Nogo, reticulon-4; T-CHO, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.