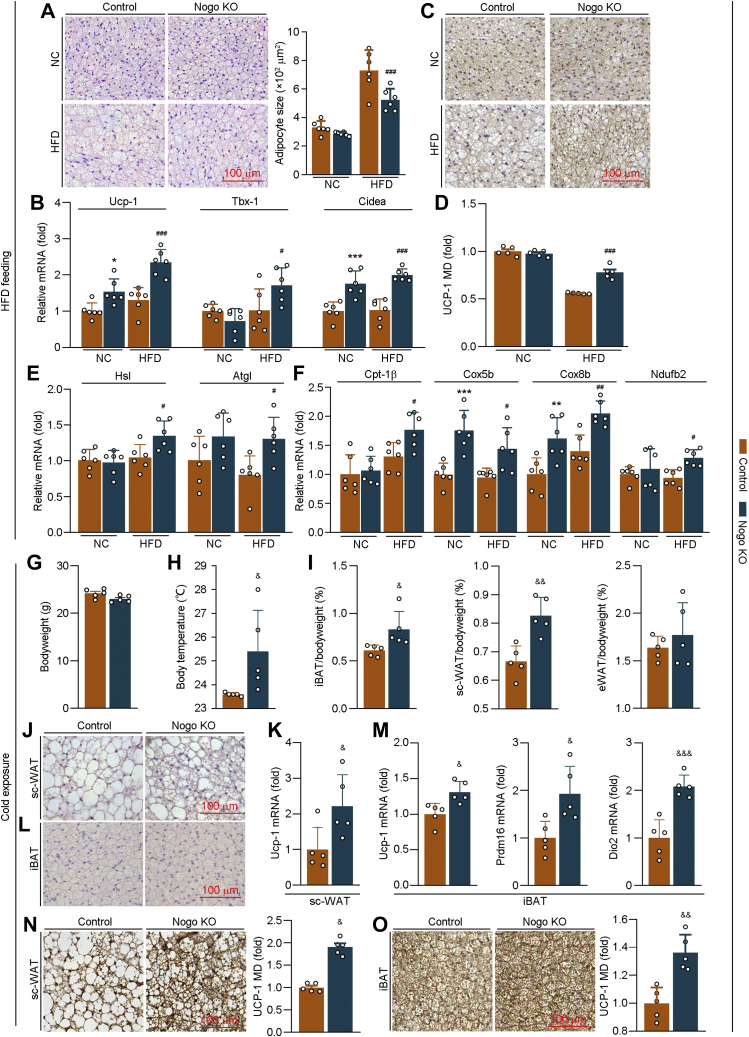
Figure 4.
Nogo deficiency enhances browning of adipose tissue in HFD feeding or cold exposure situation by promoting expression of thermogenic genes. At the end of experiment as indicated in Figure 2, iBAT was collected, and the tissue sections were conducted H&E staining with quantitation of adipocyte size (A, n = 6) and UCP-1 immunohistochemical staining (C) with quantitation of mean density (MD) (D, n = 5). Expression of thermogenic genes (Ucp-1, Tbx-1, and Cidea; B), TG hydrolysis–related genes (Hsl and Atgl; E), and fatty acid oxidation–related genes (Cpt-1β, Cox5b, Cox8b, and Ndufb2; F) were determined by qRT–PCR (n = 6). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control NC-fed mice; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus control HFD-fed mice. Male littermate control and Nogo−/− mice (∼10 weeks old, five mice per group) were housed at the 24 h cycles of 12 h at 4 °C and 12 h at room temperature for 7 days. At the end of experiment, bodyweight (G) and body temperature (H) were measured. iBAT, sc-WAT, and eWAT were collected, weighed, and calculated as percent of tissue weight in bodyweight (I). sc-WAT and iBAT sections were conducted H&E staining (J and L) and UCP-1 immunohistochemical staining with quantitation of MD (N and O). Expression of Ucp-1 in sc-WAT; Ucp-1, Prdm16, and Dio2 mRNA in iBAT were determined by qRT–PCR (n = 5; K and M). &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.01, &&&p < 0.001 versus control mice. Atgl, adipose TG lipase; Cidea, cell death–inducing DNA fragmentation factor-alpha–like effector α; Cox5b, cytochrome C oxidase subunit 5b; Cox8b, cytochrome C oxidase subunit 8b; Cpt-1β, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1β; Dio2, deiodonase 2; eWAT, epididymal white adipose tissue; HFD, high-fat diet; Hsl, hormone-sensitive lipase; iBAT, interscapular brown adipose tissue; NC, normal chow; Ndufb2, NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit b2; Nogo, reticulon-4; Prdm16, PR domain containing 16; qRT, quantitative RT; sc-WAT, subcutaneous white adipose tissue; Tbx-1, T-box transcription factor 1; TG, triglyceride; UCP-1, uncoupling protein-1.