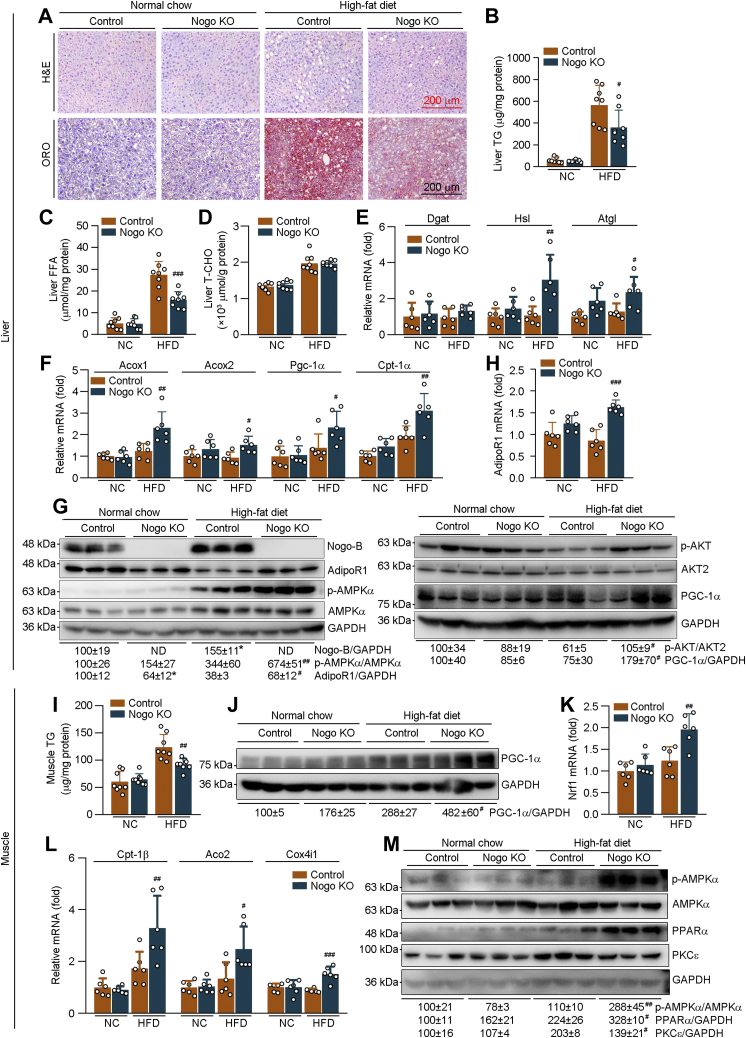
Figure 5.
Nogo deficiency inhibits HFD-induced lipid accumulation in tissues by enhancing lipid oxidation and energy metabolism. The following assays were conducted on liver or skeletal muscle samples collected from mice used in Figure 2. A, H&E and Oil red O staining was conducted on the liver sections. Hepatic TG (B), FFA (C), and T-CHO (D) levels were determined using the corresponding assay kits (n = 8). Expression of TG synthesis/hydrolysis-related genes (Dgat, Hsl, and Atgl; E), fatty acid oxidation–related genes (Acox1, Acox2, Pgc-1α, and Cpt-1α; F), and AdipoR1 (H) in the liver was determined by qRT–PCR (n = 6). G, protein expression of Nogo-B, AdipoR1, p-AMPKα, AMPKα; and p-AKT, AKT2, and PGC-1α in the liver was determined by Western blot with quantitative analysis of band density (n = 3). I, skeletal muscle TG content was determined using the TG assay kit (n = 8). J and M, protein expression of PGC-1α; p-AMPKα, AMPKα, PPARα, and PKCε were determined by Western blot with quantitative analysis of band density (n = 3). K and L, expression of Nrf1; Cpt-1β, Aco2, and Cox4i1 mRNA was determined by qRT–PCR (n = 6). ∗p < 0.05 versus control NC-fed mice; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus control HFD-fed mice. Acox, acyl-CoA oxidase; Aco2, aconitase 2; AdipoR1, adiponectin receptor 1; AMPKα, AMP-activated kinase α; Atgl, adipose TG lipase; Cox4i1, cytochrome C oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1; Cpt-1α, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1α; Cpt-1β, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1β; Dgat, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase; FFA, free fatty acid; HFD, high-fat diet; Hsl, hormone-sensitive lipase; NC, normal chow; ND, under detectable; Nogo, reticulon-4; Nrf1, nclear respiratory factor 1; p-AMPKα, phosphrylated AMPKα; Pgc-1α, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; PKCε, protein kinase C ε; qRT, quantitative RT; T-CHO, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride.