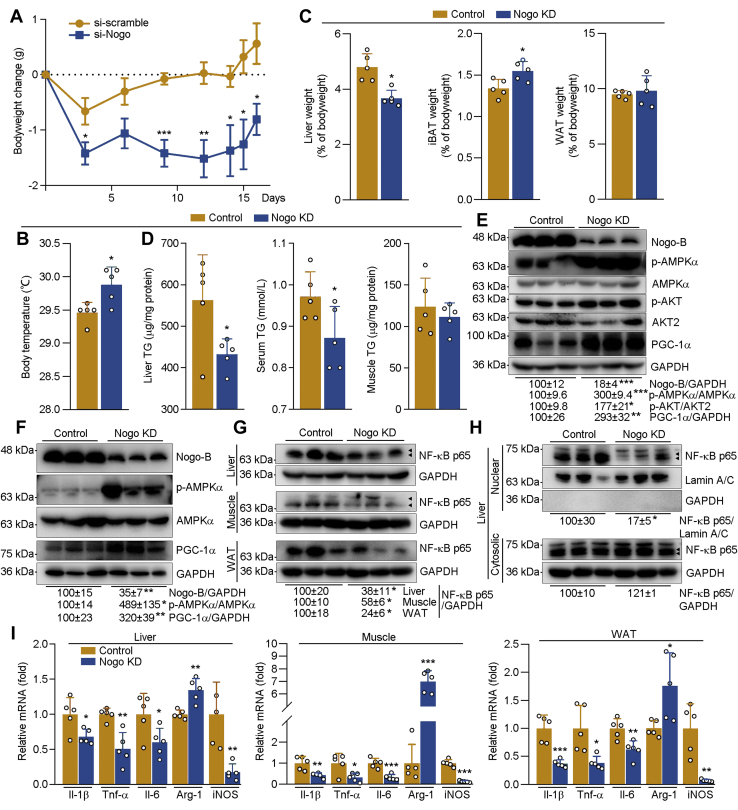
Figure 9.
Nogo siRNA ameliorates HFD-induced bodyweight gain and associated metabolic disorders in mice. After 25 weeks of HFD feeding, the obese mice (C57BL/6J, male, ∼31 weeks old) were divided into two groups (five mice per group) randomly and received tail vein injection of Nogo siRNA (Nogo KD) or scrambled siRNA (control) once every 3 days for five times. A, during the treatment, mouse bodyweight was determined at the indicated time points, and the average bodyweight change was calculated. At the end of experiment (3 days after the last siRNA injection), mouse body temperature was measured (B). After sacrifice, mouse tissues were collected for the following assays. Mouse liver, iBAT, and WAT were weighed and calculated as percent of tissue weight in bodyweight (C); TG levels in liver, serum, and skeletal muscle were determined by the assay kit or the automatic biochemical analyzer (D). Protein expression of Nogo-B, p-AMPKα, AMPKα, p-AKT, AKT2, and PGC-1α in liver or skeletal muscle (E and F), NF-κB p65 in liver, skeletal muscle, and WAT whole extract (G), liver nuclear or cytosolic extract (H) was determined by Western blot with quantitative analysis of band density; expression of Il-1β, Tnf-α, Il-6, Arg-1, and iNOS mRNA in liver, skeletal muscle, and WAT (I) was determined by qRT–PCR. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus control mice, n = 5. AMPKα, AMP-activated kinase α; Arg-1, arginase 1; HFD, high-fat diet; iBAT, interscapular brown adipose tissue; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible NO synthase; Nogo, reticulon-4; p-AMPKα, phosphorylated AMPKα; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α; qRT, quantitative RT; TG, triglyceride; Tnf, tumor necrosis factor; WAT, white adipose tissue.