Extended Data Fig. 12 |. Role of fibroblasts, potential drug targets and model of lethal COVID-19.
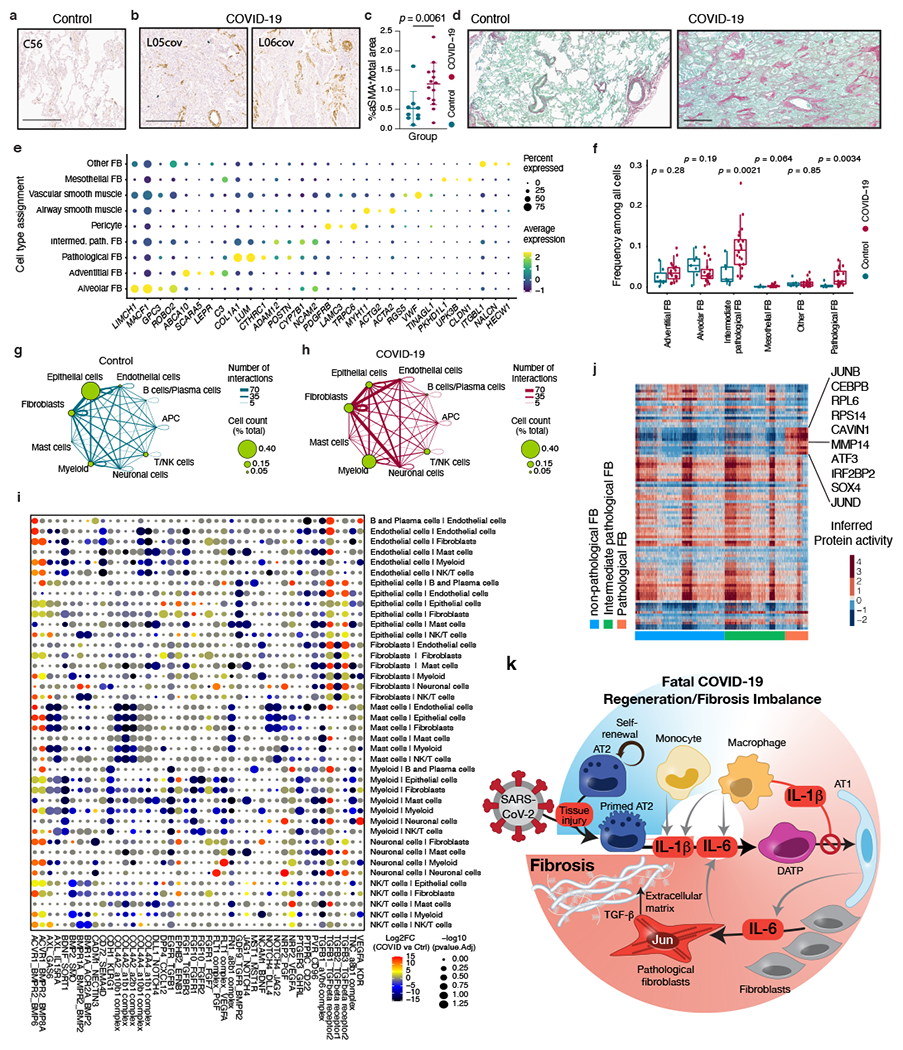
a, b, Exemplary αSMA immunohistochemical staining of tissue from control (a; sample C56; n = 7 donors) and COVID-19 samples (b; samples L05cov and L06cov; n = 17 donors). Scale bars, 500 μm. c, Percentage of α-SMA+ cells per total area (n as in a, b). Mean ± s.d., t-test. d, Exemplary Sirius red staining of control (left, n as in a) and COVID-19 (right, n as in b) samples. Scale bar, 600 μm. e, Detailed annotation of fibroblasts in this study and selected marker genes. Dot size indicates fraction of cells and colour indicates expression level (log-normalized and scaled). f, Fractions of cell types among all cells in COVID-19 (n = 19 donors examined over 20 experiments) and control lungs (n = 7 donors). Middle line, median; box edges, 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers, most extreme points that do not exceed ±1.5 × IQR. Wilcoxon rank-sum test. g, h, Inferred cell-to-cell interactions among major cell types (indicated as circles connected by lines) in control (g) and COVID-19 (h) lung samples. The size of the circle corresponds to the frequency of the respective cell type and the thickness of the lines connecting circles indicates the absolute number of interactions. i, Differential enrichment (COVID-19 versus control samples) of specific ligand–receptor interactions (rows) between two different cell types (columns). Dot colour indicates log2(fold-change) of inferred ligand–receptor expression in COVID-19 compared to control lungs (unpaired two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test); dot size is inversely correlated with Benjamini–Hochberg adjusted P (see Methods). j, Inferred protein activity (rows) among cells corresponding to pathological fibroblasts, intermediate pathological fibroblasts, and non-pathological fibroblasts (columns). Proteins with high activity in pathological fibroblasts are highlighted. k, Model summarizing potential mechanisms that contribute to morbidity and mortality in patients with COVID-19, focusing on impaired cellular regeneration and rapidly ensuing fibrosis.
