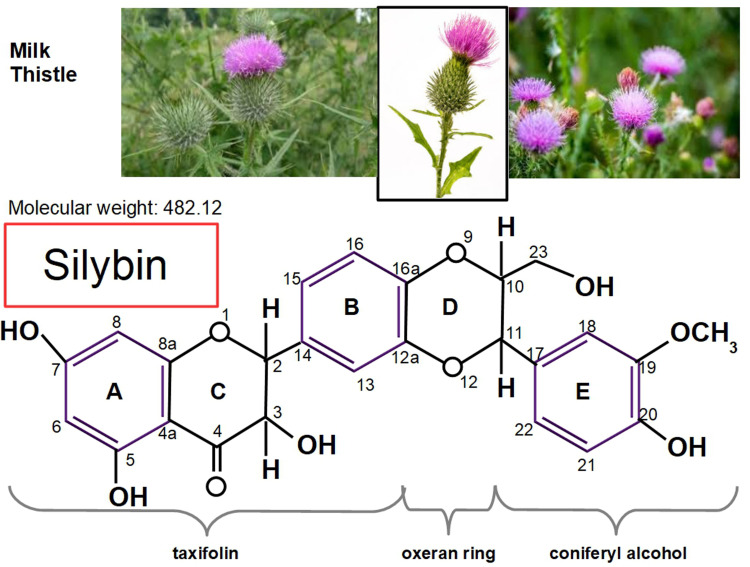
Figure 2.
Milk thistle and the chemical structure of silybin (C25 H22 O10), with its proprietary numbering. Of note, is the similarity between silybin and steroid hormones. The lower panel shows silibinin's structural formula where 3 different chemical groups can be identified: a taxifolin and a coniferyl alcohol united by an oxirane ring. According to Biedermann et al, 22 “the 20-OH group was established to be the most active radical scavenging moiety and also the most important group responsible for the lipoperoxidation inhibitory activity.” Positions 2-3 also play a role in antioxidant activity because these positions can be oxidized to produce 2-3 dehydrosilybin (see Figure 3). Silybin has 5 hydroxyl groups in positions 3, 5, 7, 20, and 23 which are the targets to produce silybin derivatives. Positions 7 and 20 are usual sites of glucuronidation of silybin during its conjugation in human metabolism.