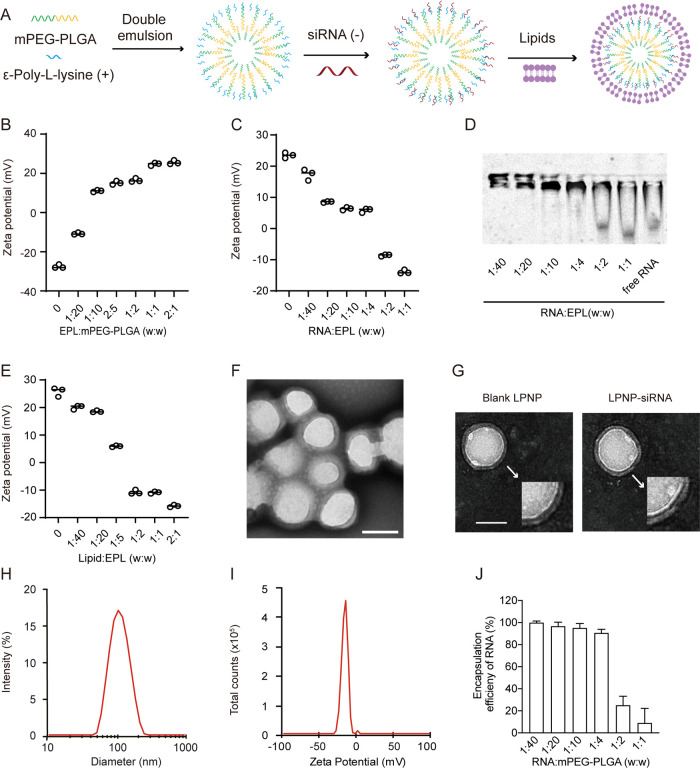
Figure 1.
Characterization of LPNP-siRNA. (A) Preparation of LPNP-siRNA. (B) Zeta potential changes of nanoparticles after modification with different amounts of ε-poly-l-lysine (EPL). (C) Zeta potential changes of EPL-modified nanoparticles loaded with different amounts of RNA. (D) Electrophoretic mobility of RNA absorbed by EPL-modified nanoparticles. (E) Changes in the zeta potentials of LPNPs after coating with a lipid bilayer shell at different mass ratios (EPL/lipid). (F, G) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of LPNP-siRNA particles and blank LPNPs; the spherical core–shell structures of the blank LPNP and LPNP-siRNA particles are shown in panel (F). (H, I) Diameter and zeta potential of LPNP-siRNA as determined by dynamic light scattering. (J) Encapsulation efficiency of RNA at various RNA/mPEG-PLGA weight ratio (n = 3). All the results are presented as means ± SD. Scale bar: 100 nm in panels (F, G).