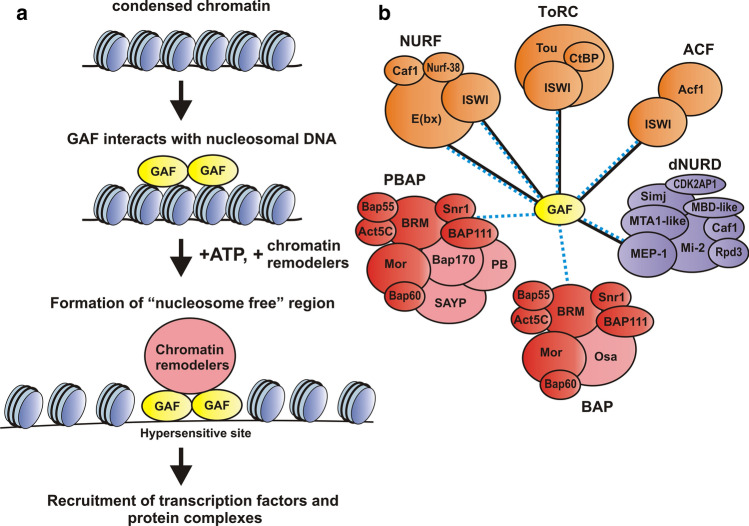
Fig. 2.
GAF functions in conjunction with ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers to establish nucleosome-free regions of chromatin. a GAF interacts with nucleosomal DNA and recruits chromatin remodelers. In an ATP-dependent reaction, remodelers translocate nucleosomes and establish “nucleosome-free” regions of chromatin that are hypersensitive to various nucleases. This facilitates the recruitment of other transcription factors. b GAF interacts with ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers of different subfamilies: SWI/SNF (PBAP and BAP), ISWI (NURF, ACF and ToRC), CHD (dNURD). Contacts established by indirect methods are indicated by dotted blue lines; direct partners (E(bx), ISWI and MEP-1) are indicated by solid black lines