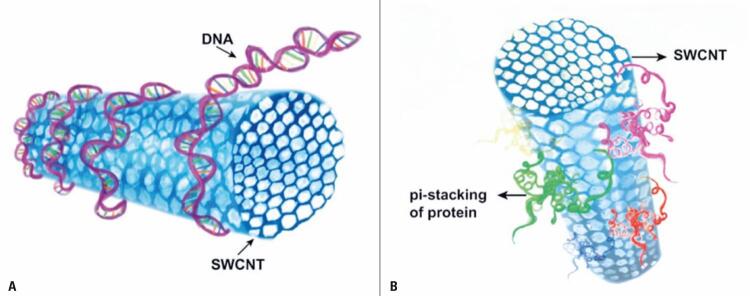
Figure 1. Models of molecular interactions between carbon nanotubes and biological molecules. (A) Interaction of DNA double helices on the surface of carbon nanotubes. The bases of nucleotides and proteins interact with carbon nanotubes by means of hydrophobic interactions or by van der Waals force, while the phosphate groups of the DNA molecule interact with water molecules. (B) Types of bonds existing between proteins and carbon nanotubes. Through p-p stacking, an interaction occurs between carbon nanotubes and the aromatic residues (Trp, Phe, and Tyr) of proteins, contributing to better adsorption and biocompatibility.
Source: Adapted from Vardharajula S, Ali SZ, Tiwari PM, Eroğlu E, Vig K, Dennis VA, et al. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: biomedical applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5361-74.(26)
SWCNT: single-walled carbon nanotubes.