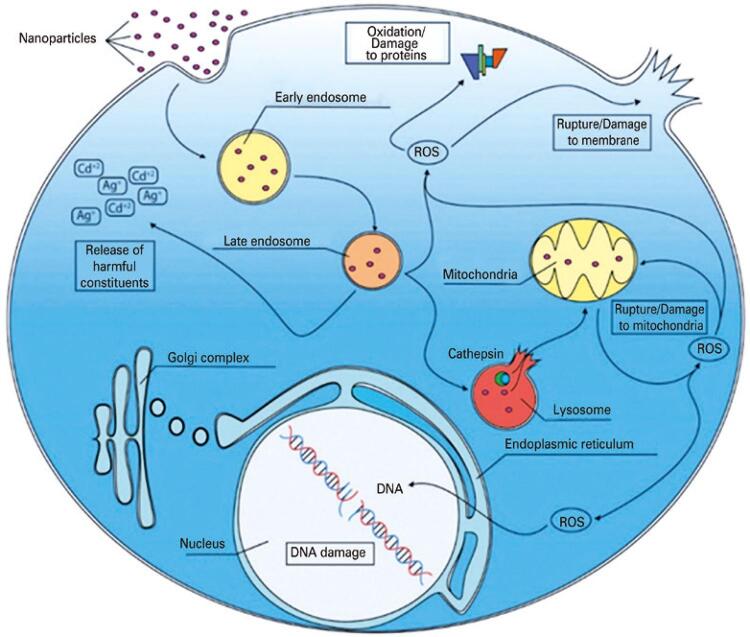
Figure 2. Main toxic effects triggered by nanostructures in eukaryotic cells. Nanoparticles can enter the cell mainly by endocytosis or by damage to cell membranes. Upon internalization and passage through the endosome-lysosome system, nanomaterials are normally degraded, releasing constituents that can generate reactive oxygen species. Reactive oxygen species have the potential to cause damage to the cell membrane, organelles, proteins, and nucleic acids, resulting in mutagenicity and cell death. Thus, reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage are considered the main mechanisms by which nanomaterials induce toxicity.
Source: translated from Radaic A, Pugliese, GO, Campese GC, Pessine FB, Jesus MB. Como estudar interações entre nanopartículas e sistemas biológicos. Quim Nova. 2016;39(10):1236-44. Review. Figura 3, Principais efeitos tóxicos desencadeados por nanomateriais em células eucarióticas; p. 1242.(30)