Table 1.
Prevention, Assessment and Treatment Strategies for Chronic Comorbidities in HIV
| Chronic Condition | HIV Risk | Prevention Strategies | Monitoring/Assessment Strategies | Treatment Strategies | Structural Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASCVD | 1.5- to 2-fold greater risk | ↓ Hypertension, ↓Hypocholesteremia ↓ Hyperglycemia ↓ Weight 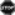 Smoking Smoking↑Physical activity ↑ Healthy diet |
|
|
Shift to collaborative care models to include cardiovascular specialist, pharmacist, registered dietician, physical therapy |
| COPD | ~10% higher risk |
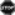 Smoking (consider using the 5 As) Smoking (consider using the 5 As)↓ exposure to environmental pollutants
|
|
|
Collaborative care models to include respiratory specialist, pharmacist, smoking cessation counselor Support community and workplace initiatives to reduce tobacco use (e.g., tobacco-free zones, tobacco/vaping taxes, age of purchase) |
| Lung Cancer | ~2-fold greater risk (Hernández-Ramírez et al., 2017) |
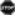 Smoking (consider using the 5 As) Smoking (consider using the 5 As)↑Physical activity ↑ Healthy diet |
|
|
|
| Liver Cancer | 4-fold higher risk | ↓Injection drug use ↓Alcohol & tobacco use ↑Safe sex Administer Hepatitis B vaccine |
|
|
Collaborative care models to include hepatology, pharmacist, substance use/behavioral medicine specialist Support use of needle exchanges |
| Anal Cancer | 19-fold higher risk |
|
|
|
|
| Diabetes Mellitus | ~2-fold reduced risk in HIV, but growing (Herrin et al., 2016) | ↓ Hyperglycemia ↓ Weight ↑Physical Activity ↑ Healthy Diet |
|
|
Adopt collaborative care models to include endocrinology, nephrology, pharmacy, registered dietetics, physical therapy Support increased access to promote food security including SNAP |
Note. ASCVD – Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, COPD – Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder, 5 As – Ask, Assess, Advise, Agree, Assist, HPV – Human Papillomavirus, PLWH – People Living with HIV, SNAP - Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program

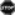 Smoking
Smoking