Abstract
In the era of evidence-based medicine, real-world evidence (RWE) studies have opened avenues to utilize real-world data (RWD) effectively for improving clinical decision-making. However, the transformation of RWD into a meaningful RWE can only be achieved when the researcher asks the right clinical question, selects the right RWD source for variables of interest, uses the right study design, and applies the right statistical analysis. The generated RWE needs to have internal as well as external validity to be actionable. The “fit-for-purpose” observational study designs include descriptive, case–control, cross-sectional, and cohort. This article focuses on the advantages and disadvantages including the inherent bias of each study design. The RWE study decision guide has also been provided to aid the selection of appropriate study designs.
Keywords: Bias, observational, real-world evidence, study designs
INTRODUCTION
The evolution of real-world evidence (RWE) over the past years has improved our understanding of disease characteristics as well as the safety and effectiveness of treatment in clinical practice. Well-designed RWE may complement the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in clinical decision-making. Digitalization of health-care systems advances the availability and utilization of real-world data (RWD), such as electronic medical records, registries, and wearable devices, by researchers. The generated RWE needs to be internally valid and generalizable to an identifiable target population to be actionable.[1] Turning RWD into RWE involves the interplay of a design layer – study design appropriate for the research question; a measurement layer – transforming the patient-level data into the variables of exposure and outcome; and an analysis layer – deriving the estimate of effect.[1] We will discuss RWE studies with focus on observational designs and the selection of appropriate designs that guide investigators and reviewers of RWE.
REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE STUDY DESIGNS
RWE studies can be classified basis the assignment of intervention and requirement of the comparison group [Figure 1 and Table 1].[2]
Figure 1.
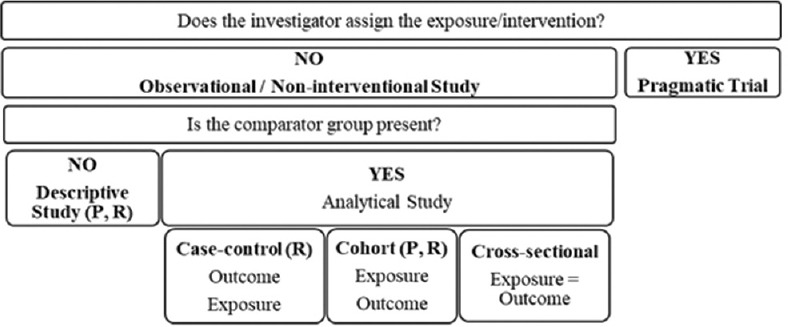
Classification of real-world evidence study designs; R – retrospective, P – prospective
Table 1.
The design and analysis time frame (relative to the study start or index date) of different types of real-world evidence studies
| Retrospective | Present | Prospective |
|---|---|---|
| Noninterventional case-control study | Cross-sectional study | Noninterventional cohort study with primary data |
| Noninterventional cohort study with secondary data | Registry | |
| Administrative or claims database study | ||
| Electronic health record study |
In the observational study, the participants are not preassigned to exposure or an intervention. The choice of treatments is up to patients and their physicians.
In a retrospective observational study, both exposure and outcomes have already occurred. In subsequent sections, we shall discuss in detail about 3 retrospective observational study designs, namely cross-sectional, case-control, and cohort.
Cross-sectional studies
Cross-sectional studies involve the simultaneous assessment of exposure and outcome in a single group of patients at a specific point in time. They are typically used to assess the prevalence and infer the cause of conditions/outcomes.[2] The general design involves defining the target population, deriving a sample of that population, and defining the characteristics being studied. The definition of the condition and health characteristics under study should be standardized, reproducible, and feasible to apply on a large scale.[3]
Datta et al.[4] conducted a community-based descriptive cross-sectional study among individuals aged 30 years and above in urban field practice area of a tertiary care hospital. Pretested questionnaire was used to measure the prevalence of self-reported hypertension over the past 2 years.
Advantages
Disadvantages
As the data are collected at a single time point, a temporal relationship between the exposure and the outcome cannot be ascertained,[2] for example, if the cross-sectional study demonstrates an association between obesity and arthritis, for example, one cannot prove causal relationship whether arthritis led to obesity or the obesity caused arthritis or, whether some third factor caused them both.
Susceptible to selection bias, for example, patients who develop an outcome but die before the end of the study are not captured[2]
Unsuitable for studying rare diseases or for diseases of short duration due to low prevalence at a single point in time[3]
Often completed using questionnaires, which have inherent problems, including low response rates and susceptibility to various sources of bias.[2]
Case–control studies
Case–control studies are typically retrospective studies (”backward looking”) because the approach is to identify persons with the disease of interest and then look backward in time to identify factors that may have caused it [Figure 2].[3] Cases are the patients with the outcome of interest, and controls are matched groups of patients without this outcome derived from the same population. The exposure to potential causal variables such as risk factors and treatment are evaluated basis of the medical history to determine causality. Case–control studies have a longitudinal or temporal aspect to the data that cross-sectional studies do not.[3] To have the consistency of the associations and risk estimates between a case-control study and other types of studies, the three key assumptions need to be met:[3]
Figure 2.
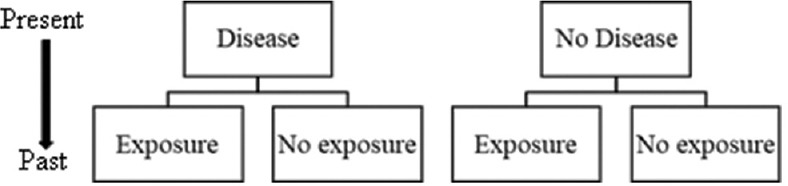
Design of case-control study
cases are representative of all the cases,
controls are representative of persons without the disease, and
data are collected similarly in cases and controls.
The case–control studies help answer the research question leading to hypothesis generation.[2]
Swain et al.[5] conducted a population-based case–control study. Cases (disease) were confirmed dengue fever patients tested through IgM method and hospitalized to any public or private health facilities of the state, and controls (no disease) were from same living area of cases matched with sex and age (±2 years) with no history of dengue, chikungunya or acute febrile illness in the last 1 year. A structured validated questionnaire was used to collect information regarding exposures such as environmental practices and travel history for each consenting participant.
Advantages
Suitable for rare outcomes or those with a long latency between exposure and disease[2]
Simultaneous assessment of multiple etiologic factors or potential predictors of the specific outcome[2]
The sample size requirement for the same effect size would be higher for a cohort study than that for a case–control study. Further, the lower prevalence of disease may result in much higher sample size of a cohort study but may not have significant impact on that for a case–control study.[3]
Disadvantages
The study typically involves a single outcome[2]
No information about the base population from which the cases are drawn; so incidence and prevalence cannot be estimated[3]
Table 2.
Bias in case–control studies
| Type of Bias | Description of Bias |
|---|---|
| Volunteer bias or “healthy volunteer” effect | Significant differences in characteristics and behavior of study volunteers from those of nonvolunteers |
| Prevalence or incidence bias | Missing the subjects who experienced the outcome/exposure for a short duration or a fatal episode remotely in the past |
| Membership bias or “healthy worker” or “healthy migrant” effect | A specific group of people, for example, employed or migrant population, may systematically differ in quality of health from that of the general population; this bias can be controlled by taking controls from the same worker or migrant population |
| Diagnostic/exposure suspicion bias | Information about a subject’s disease status, such as the thromboembolic episode in a woman, influences both the intensity and the outcome of a search for exposure to a putative cause, such as the use of contraceptive pills |
| Recall bias | The cases may have better recall/memory of any possible exposure that could have caused their illness than the controls |
| Family information bias | A new case triggers the flow of information about exposures and illnesses within a family, for example, a rare familial condition that is never mentioned until a family member begins to demonstrate some of the same symptoms |
Cohort studies
Cohort studies evaluate the association between a particular exposure or a risk factor and subsequent development of disease [Figure 3]. They are “prospective” (”forward looking”) in that exposure or risk factor information is collected about 2 cohorts (exposed and nonexposed), and then both cohorts are followed up to ascertain the development of the outcome. In concurrent cohort studies, people with or without exposures are identified at the initiation of the study and information is collected looking forward in time to identify disease outcomes. In nonconcurrent cohort studies (retrospective), exposure information has already been collected at some point in the past and participants are surveyed in the present to determine the presence or absence of disease. It has the advantage of providing long follow-ups without waiting for time to pass to obtain disease outcomes.
Figure 3.
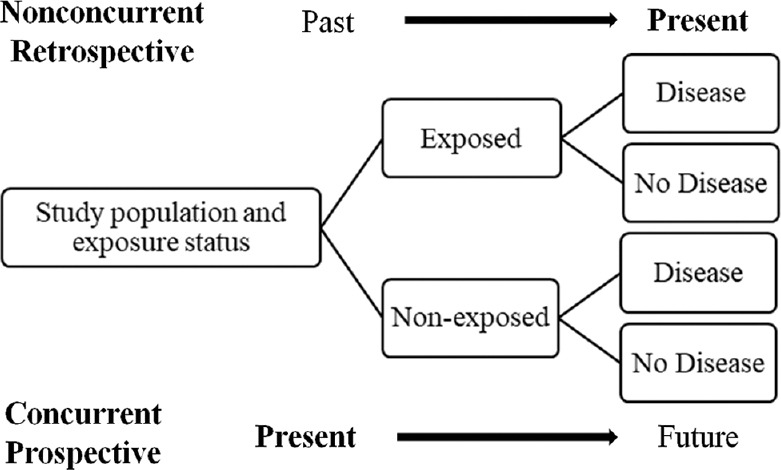
Concurrent and nonconcurrent cohort study design. Adapted from Johnson 2018[3]
Badyal et al.[6] conducted a prospective, observational, multicenter cohort study among health-care workers [HCW] (HCWs; likely to be exposed to COVID-19 cases) who were either taking or not taking prophylactic treatment (Exposure) for COVID-19 and assessed their COVID-19 positivity by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (Disease).
Nested case–control study is a special study design that reduces most biases related to selection and data collection, which is typically seen in classic case–control studies, by selecting cases and controls from within a large-scale prospective cohort study. The biologic samples in the ongoing cohort study can be collected and stored until enough cases have accumulated to provide adequate study power. At that time, these baseline samples from the newly occurring cases can be thawed and measured, along with a comparison group of matched (or unmatched) controls, allowing a much more efficient approach to examining expensive or difficult-to-measure risk factors.[3]
Figure 4.
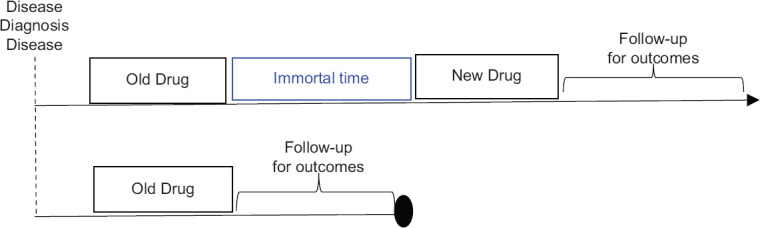
Immortal time bias. Adapted from Franklin et al., 2017[7]
Nested case-cohort designs sample a priori so regardless of case status or time. This design is used for the analysis of “time to event/failure” in a large cohort where that event/failure is rare and enormous resources may be needed to ascertain covariate values. Nested case–cohort designs are more flexible than nested case–control designs when there are different choices for the time axis or several failure time outcomes.[3]
Advantages
Find incident (new-onset) cases, rather than prevalent (existing) cases
Provide more information about the natural history of disease as well as direct estimates of incidence and relative risk
Firmly establish the temporal relationships between exposure and disease
Multiple disease outcomes can be studied in relationship to the exposure
Suitable to study a rare exposure, with exposed persons gathered at the beginning of the study.
Disadvantages
Concurrent cohort design: Study duration may be exceedingly long, making difficult the maintenance of consistent study methods and enthusiasm of staff and participants
Follow-up of free-living populations may be expensive because people move or change their contact information and can be difficult to track
Requirement of large samples size and more so for rare diseases
Table 3.
Bias in cohort studies
| Type of Bias | Description of Bias |
|---|---|
| Selection bias | A systematic error in creating intervention groups, causing them to differ with respect to measured or unmeasured baseline characteristics, and ultimately prognosis |
| Adjustment for causal intermediates | Adjusting for variables on the causal pathway between treatment and outcome can result in biased estimation of both the total effect of treatment and the direct effect that is not mediated through the adjustment variables |
| Immortal person-time bias | Occur whenever information assessed during follow-up is used to determine a patient’s inclusion or exclusion in the study or treatment group assignmentFor example, when assessing a new drug vs. an old comparator drug, some cohort studies first identify all patients receiving the new drug to maximize the size of this group, and then identify patients receiving the old comparator drug who never receive the new drug, beginning follow-up at the initiation of the relevant treatment for each group [Figure 4]. Patients who survived ‘immortal time’ on an old drug were switched to the new drug, and selectively excluded from the comparator group, making the old drug appear worse |
| Depletion of susceptibles or “survivorship bias” | In the Nurses’ Health study, prevalent users of HRT were followed for outcomes and compared with nonusers. Because the HRT group included many patients who had been on treatment for several years, it effectively excluded cardiovascular events occurring shortly after therapy initiation, leaving a cohort of hormone users that were less susceptible to the outcome |
| Reverse causation | When an apparent association between treatment and outcome is because outcome status influences treatment choice, rather than treatment impacting the outcome. |
HRT=Hormone therapy
Selection of right real-world evidence study design
A well-conducted RWE has both successfully replicated and predicted findings of RCTs. Transparency in the conduct and presentation of RWE studies is critical to allow reviewers to evaluate the study's validity and have confidence in their decision-making.[1]
The decision guide for selection of RWE study design (modified from the RWE Framework flow diagram developed by Xia et al. 2019[9]) has been provided in Table 4.
Table 4.
Real-world evidence study decision guide
| What is your research question? |
| What is the research area of interest? |
| Disease |
| Drug/device |
| Other |
| What is the setting of study conduct? |
| Routine practice |
| Altering of routine practice |
| What are the outcomes of interest? |
| Are the data of interest recorded in routine practice? |
| Primary data collection and need for randomization |
| Secondary data analysis |
| Hybrid |
| What is the directionality of data review and analysis? |
| Retrospective |
| Prospective |
| Hybrid |
| What is the appropriate RWE study design? |
| Case–control |
| Cohort |
| Cross-sectional |
| Pragmatic trial |
| RWE study question – PECO or PICO |
| Population |
| Exposure/intervention |
| Comparison |
| Outcome |
Modified from the RWE Framework flow diagram developed by Xia et al. 2019. RWE=Real-world evidence, PECO=Population, Exposure, Comparator, Outcome, PICO=Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcome
CONCLUSION
The digitization of medical informatics has opened new avenues for the conduct of retrospective RWE studies. Observational RWE studies are less expensive and can be conducted quickly compared to the RCTs. However, observational RWE studies can be used only to find associations between risk factors and outcomes, but alone they cannot establish causation. In addition, there are inherent biases and issues of confounding associated with the observational studies impacting the “internal validity” of these studies. Well-designed and conducted observational RWE studies with careful analysis and interpretation will overcome most of these challenges and may help in hypothesis generation or complement the RCTs.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Schneeweiss S, Patorno E. Conducting real-world evidence studies on the clinical outcomes of diabetes treatments. Endocr Rev. 2021;42:1–33. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnab007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Camm AJ, Fox KA. Strengths and weaknesses of 'real-world' studies involving non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants. Open Heart. 2018;5:e000788. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Johnson LL. Principles and Practice of Clinical Research. 4th ed. Academic Press: Elsevier; 2018. Design of observational studies; pp. 231–48. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Datta S, Sahu SK, Niranjjan R, Roy G. A community-based cross-sectional study on hypertension screening in Puducherry, India. Indian J Med Res. 2019;150:199–202. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1877_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Swain S, Bhatt M, Biswal D, Pati S, Soares Magalhaes RJ. Risk factors for dengue outbreaks in Odisha, India: A case-control study. J Infect Public Health. 2020;13:625–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2019.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Badyal D, Chandy S, Chugh P, Faruqui A, Gupta YK, Hazra A, et al. Hydroxychloroquine for SARS CoV2 prophylaxis in healthcare workers – A multicentric cohort study assessing effectiveness and safety. J Assoc Physicians India. 2021;69:11–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Franklin JM, Schneeweiss S. When and how can real world data analyses substitute for randomized controlled trials? Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;102:924–33. doi: 10.1002/cpt.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lu CY. Observational studies: A review of study designs, challenges and strategies to reduce confounding. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63:691–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2009.02056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xia AD, Schaefer CP, Szende A, Jahn E, Hirst MJ. RWE framework: An interactive visual tool to support a real-world evidence study design. Drugs Real World Outcomes. 2019;6:193–203. doi: 10.1007/s40801-019-00167-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


