Figure 4: Diagnostic performance of HRME using a multi-task CNN.
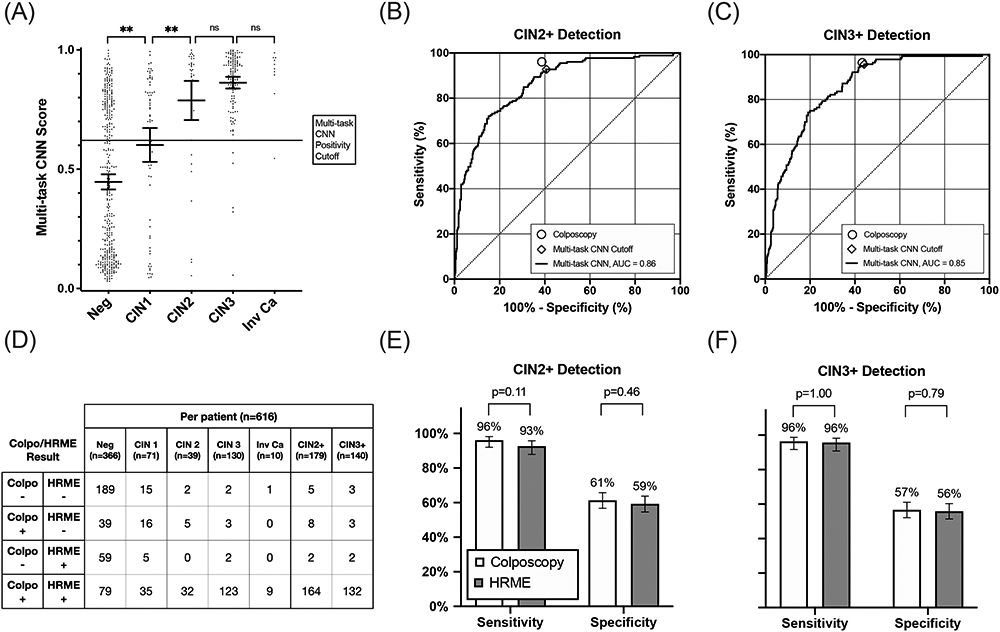
(A) Per-patient HRME multi-task CNN scores stratified by histopathology result. The solid line represents the cutoff for positivity by multi-task CNN for comparison with colposcopy (low-grade or more severe). Bars overlaid on scatter plots indicate mean and 95% confidence intervals within each column. (B-C) Receiver operator characteristic curves of HRME with multi-task CNN analysis for detection of CIN2+ and CIN3+. Performance of colposcopy (low-grade or more severe) are HRME with multi-task CNN analysis using the post-hoc positivity threshold are plotted on ROC curves for reference. (D) Cross tabulation of outcomes for colposcopy (low-grade or more severe) and multi-task CNN HRME classification by pathology result for each patient. (E-F) Comparisons of the sensitivity and specificity of colposcopy and HRME with multi-task CNN analysis for detection of both CIN2+ and CIN3+. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. The following symbols indicate p-value results as follows: ns (P>0.05), *(P≤0.05), **(P≤0.01).
