FIGURE 7.
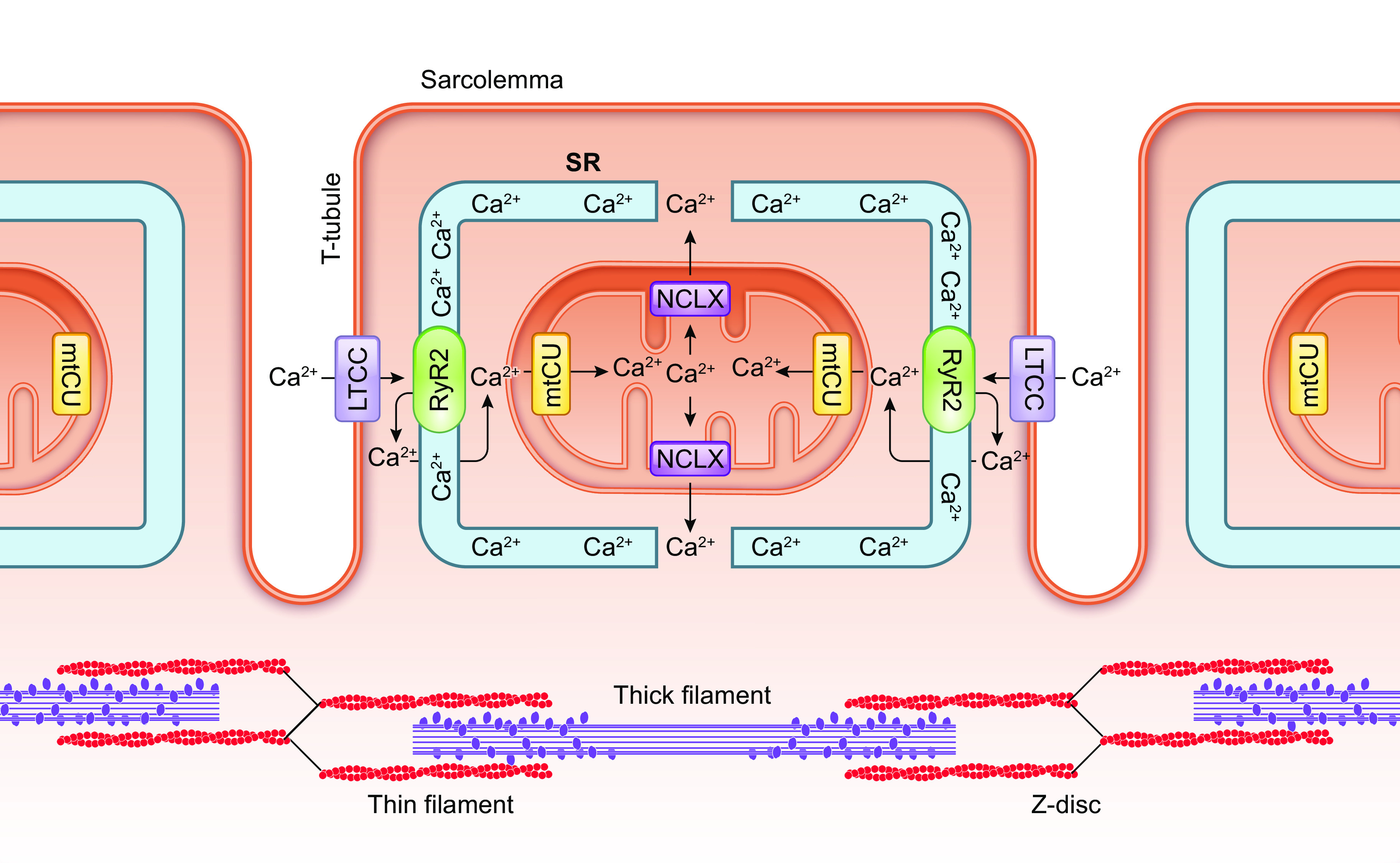
Spatial segregation of mitochondrial Ca2+ influx and efflux pathways in cardiomyocytes. In cardiac muscle, the mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex (mtCU) is found at regions of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) near contacts between the outer mitochondrial membrane and Ca2+ release sites on the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR). This arrangement enables Ca2+ released from the SR via the ryanodine receptor (RyR2) to be taken up efficiently into the mitochondrial matrix. NCLX, the principal route for mitochondrial Ca2+ efflux in cardiomyocytes, is instead distributed at regions of the IMM that are more distant from the sites of SR-mitochondria contact. This spatial separation of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and efflux is thought to minimize futile cycling of Ca2+ flux through the mtCU and NCLX that would otherwise depolarize mitochondrial membrane potential. See glossary for abbreviations.
