Figure 2.
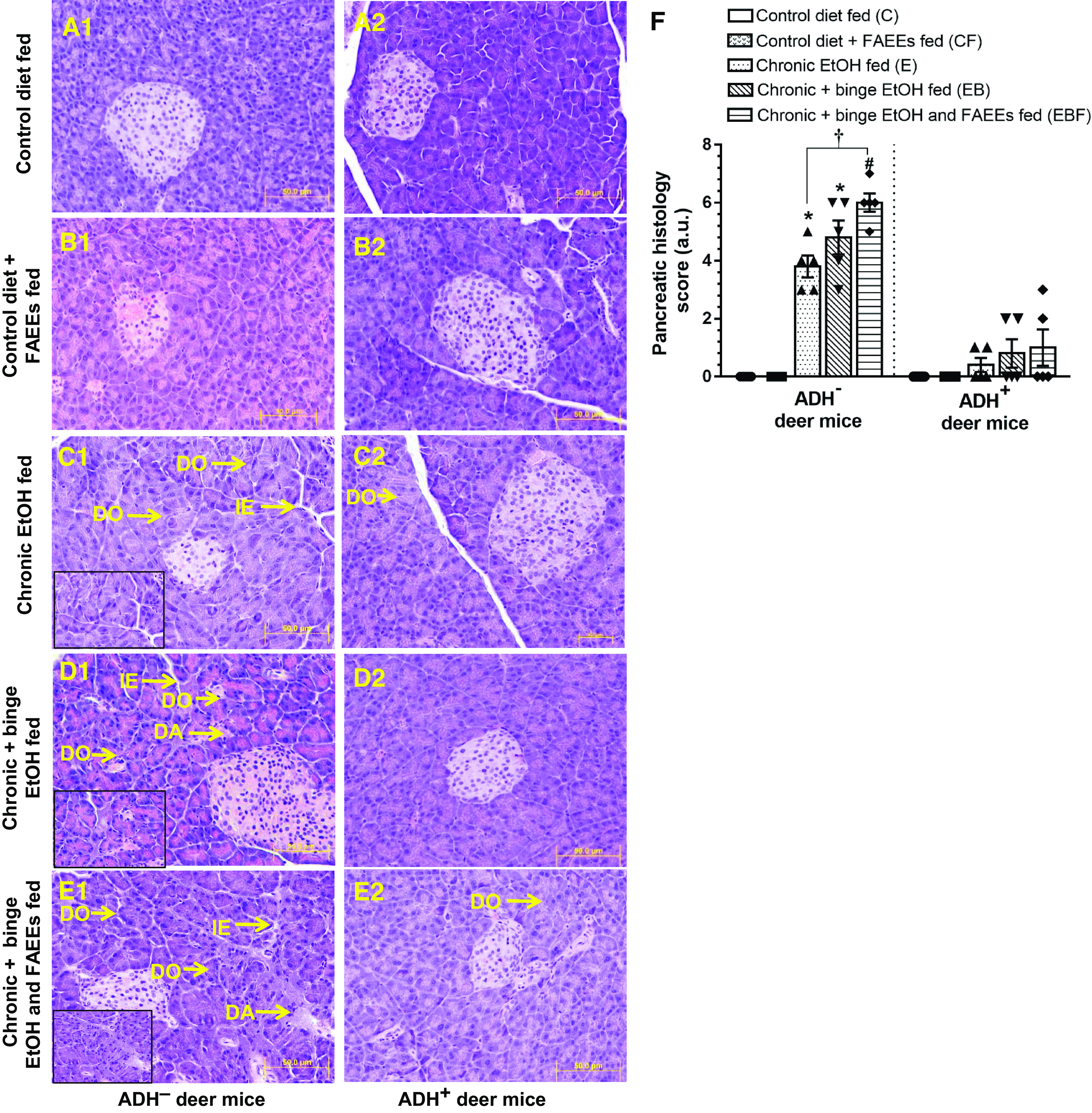
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained representative pancreatic tissue sections of ADH− (A1–E1; left) and ADH+ deer mice (A2–E2; right), respectively. Pancreas of ADH− and ADH+ deer mice pair-fed control diet (A1 and A2) or with FAEEs (B1 and B2) showing normal histology. Chronic EtOH-fed ADH− deer mice (C1) show disorganization (DO) of acinar cells and interstitial edema (IE). A mild disorganization (DO) of acinar cells was also observed in chronic EtOH-fed ADH+ deer mice (C2). Pancreas of chronic plus binge EtOH-fed ADH− deer mice shows a significant acinar disorganization (DO) along with degenerative changes (DA), and interstitial edema (IE) (D1), as compared with normal histology in chronic plus binge EtOH-fed ADH+ deer mice (D2). Pancreas of chronic plus binge EtOH and FAEEs-fed ADH− deer mice shows a remarkable disorganization (DO) and degenerative changes (DA) in acinar structure and interstitial edema (IE) (E1) as compared with the pancreas of chronic plus binge EtOH and FAEEs-fed ADH+ deer mice (E2). Inset shows area of higher magnification (X40). (Original magnification ×20, bar = 50 μm, n = 5 mice/group). Cumulative histology score (F) in the pancreas of ADH− and ADH+ deer mice. Data were analyzed using ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, and presented as means ± SE (n = 5 replicates). *P ≤ 0.05 chronic EtOH-fed group and chronic plus binge EtOH-fed group vs. pair-fed control diet group. #P ≤ 0.05 chronic plus binge EtOH and FAEEs-fed group vs. control diet plus FAEEs-fed group. †P ≤ 0.05 chronic plus binge EtOH and FAEEs-fed group vs. chronic EtOH-fed group. ADH−, alcohol dehydrogenase-deficient; FAEEs, fatty acid ethyl esters.
