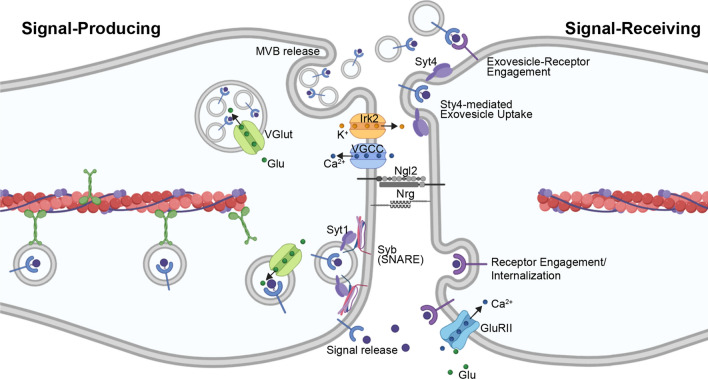
Fig. 5.
Glutamatergic Signaling at Morphogenetic Synapses. Cytonemes from a signal-producing cell are primed for signaling through uptake of glutamate molecules (green circles) through the Vesicular Glutamate Transporter (VGlut). At the cytoneme membrane, Ca2+ ions (blue circles) are imported by the Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (VGCC) and K+ ions (orange circles) are exported by Inward-Rectifying K+ Channel (Irk2) to establish an ion gradient. The Ca2+-binding protein Synaptotagmin 1 (Syt1) targets signal-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane for vesicle docking by Ca2+-dependent R-SNARE family members. Release of vesicular contents (signals and/or exosomes) at the synapse results in release of glutamate into this site. Glutamate binds the non-NMDA ionotropic glutamate receptor (GluRII) to promote its activity for Ca2+ uptake by the signal-receiving cell. Ca2+-binding Synaptotagmin 4 (Syt4) functions on the extracellular surface of the signal-receiving cytoneme to facilitate signal reception. The neuronal synaptic adhesion protein Neuroligin 2 (Nlg2) and neuronal CAM Neuroglian (Nrg) function on the ASP to stabilize this interaction