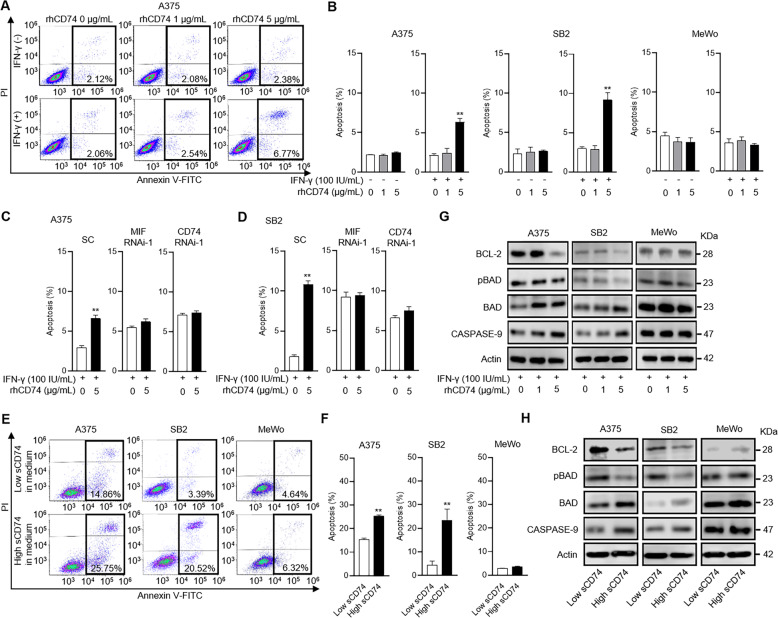
Fig. 5. sCD74 exerts pro-apoptotic functions by inhibiting MIF–CD74 interaction.
A Representative flow-cytometry plots show annexin V–FITC (x axis) and PI (y axis) in A375. B The rate of apoptotic cells in A375, SB2, and MeWo quantified by flow cytometry (n = 3). C, D The rate of apoptotic cells in A375 (C) and SB2 (D) transfected with SC siRNA, MIF RNAi-1, or CD74 RNAi-1 quantified by flow cytometry (n = 3). Flow cytometry (A–D) was performed 72 h after the administration of 0 or 5 µg/mL rhCD74 under 100 IU/mL IFN-γ stimulation. E Representative flow-cytometry plots show annexin V–FITC (x axis) and PI (y axis) in A375, SB2, and MeWo. F Rate of apoptotic cells in A375, SB2, and MeWo (n = 3). Flow cytometry (E, F) was performed 48 h after coculture with THP-1 MΦ. High and low concentrations of sCD74 in medium were obtained by transfecting SC siRNA or CD74 RNAi-1 to THP-1 MΦ, respectively, in the presence of 100 U/mL IFN-γ. G WB analysis of BCL-2, pBAD, BAD, and CASPASE-9 in A375, SB2, and MeWo 72 h after treatment with different concentrations of rhCD74 (0, 1, and 5 µg/mL) under 100 IU/mL IFN-γ stimulation. Actin and BAD were used as loading controls. H WB analysis of BCL-2, pBAD, BAD, and CASPASE-9 in A375, SB2, and MeWo 48 h after coculture with THP-1 MΦ. Actin and BAD were used as loading controls. Graph values represent mean ± SD. Significance in difference between two groups was tested by Student t-test. **p < 0.01. IFN-γ interferon-γ, MIF macrophage-migration inhibitory factor, MΦ macrophage, PI propidium iodide, rh recombinant human, SC scramble, SD standard deviation, siRNA short-interference RNA, WB Western blot.