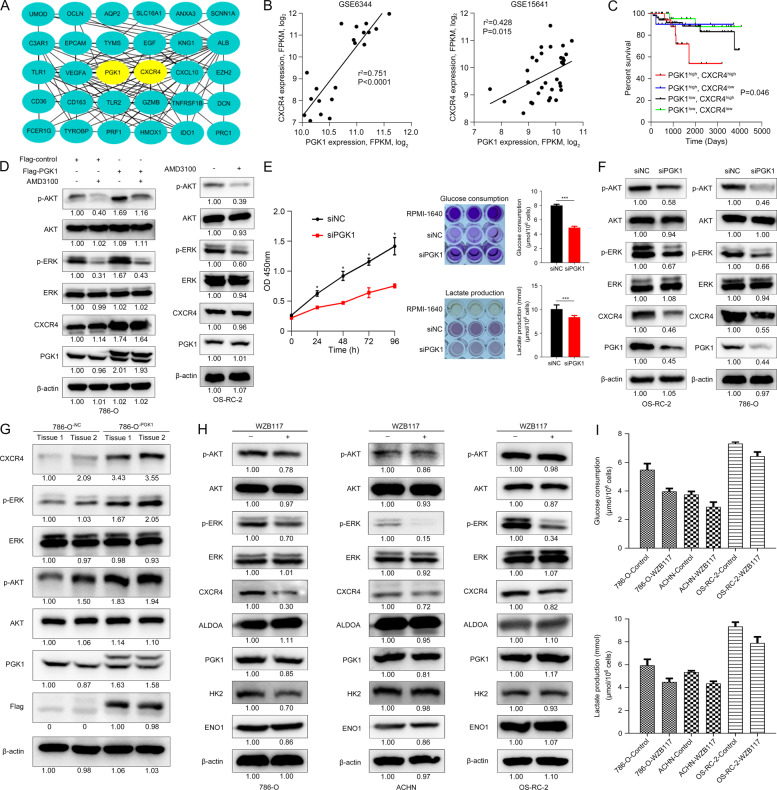
Fig. 6. PGK1 activates CXCR4/ERK pathway in KIRC cells / tissues.
A PGK1 and CXCR4 were the hub genes in KIRC, and there was a strong correlation between PGK1 and CXCR4. B Co-expression of PGK1 and CXCR4 transcript levels from GSE6344 and GSE15641 dataset. C Kaplan–Meier’s survival analysis of the correlation between the combination of PGK1 and CXCR4 expression levels and disease-free interval (DFI) survival from TCGA KIRC objects. D PGK1 induced the CXCR4-mediated phosphorylation of AKT (p-AKT) and ERK (p-ERK), and blockade of CXCR4 signaling by AMD3100 treatment did not alter cellular PGK1 expression in KIRC cells. E PGK1 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and decreased glucose consumption and lactate production in OS-RC-2 cells. The darker the color develops, the more glucose remaining and lactate produced. F CXCR4, p-AKT, and p-ERK were decreased by PGK1 inhibition in 786-O and OS-RC-2 cells. G Protein levels of PGK1, CXCR4, p-AKT, and p-ERK were detected in xenograft tumors inoculating 786-O-PGK1 cells. β-actin served as the internal control. Glycolysis suppression by 40 μM WZB117 treatment for 48 h significantly downregulated CXCR4 and p-ERK (H) and reduced glucose consumption and lactate production (I) in RCC cells.