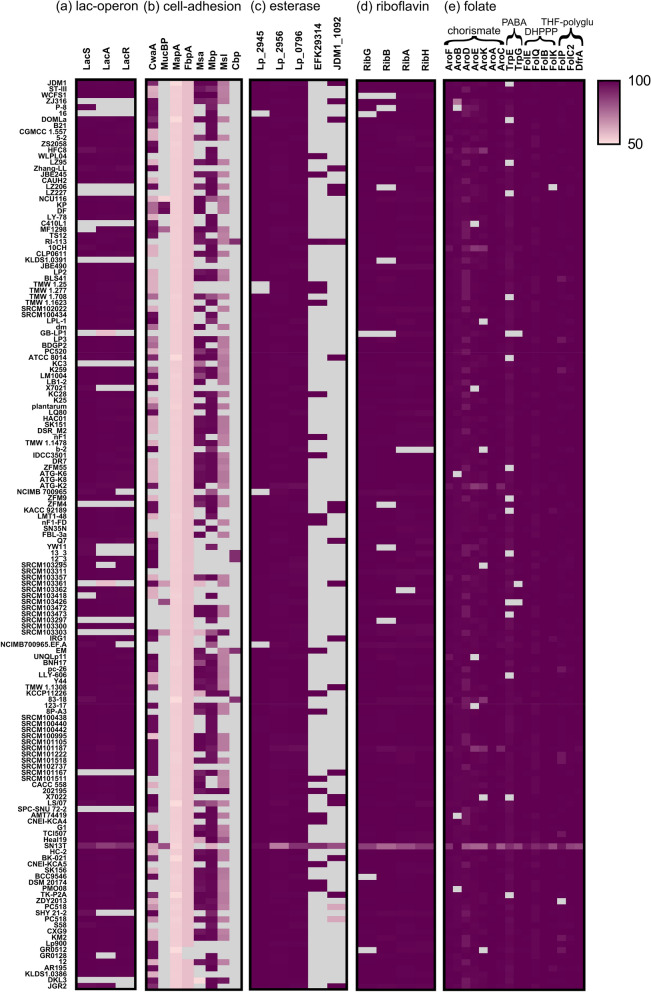
Figure 3.
Comparative genomics of L. plantarum strains for the presence of genes encoding proteins related to lactose utilization, adhesion, metabolism of phenolics, and vitamin biosynthesis. BLASTp results depicted as heatmaps with grey color denoting no hit and pink to dark purple gradation denoting presence of genes with 50%-100% identity with the query sequences. (a) Lac operon, LacS: lactose and galactose permease, LacA: β-galactosidase, LacR: lactose transport regulator. (b) Cell-adhesion related proteins, CwaA (cell wall-anchored adhesion-associated protein), MucBP (mucin-binding protein), MapA (mucus adhesion-promoting protein), FbpA (fibronectin-binding protein A), Msa (mannose-specific adhesin), Mub (mucus-binding protein precursor), Msl (mannose-specific lectin), and Cbp (collagen-binding protein). See Table S3 for the details of the proteins used as the query sequences. (c) Esterases characterized from L. plantarum, Lp_2945 (Gallate decarboxylase from WCFS1), Lp_2956 (Tannase from WCFS1, Lp_0796 (Esterase from WCFS1), EFK29314 (Tannase from ATCC14917) and JDM1_1092 (Esterase from JDM1). (d) Riboflavin and (e) folate biosynthesis proteins, adapted from36.