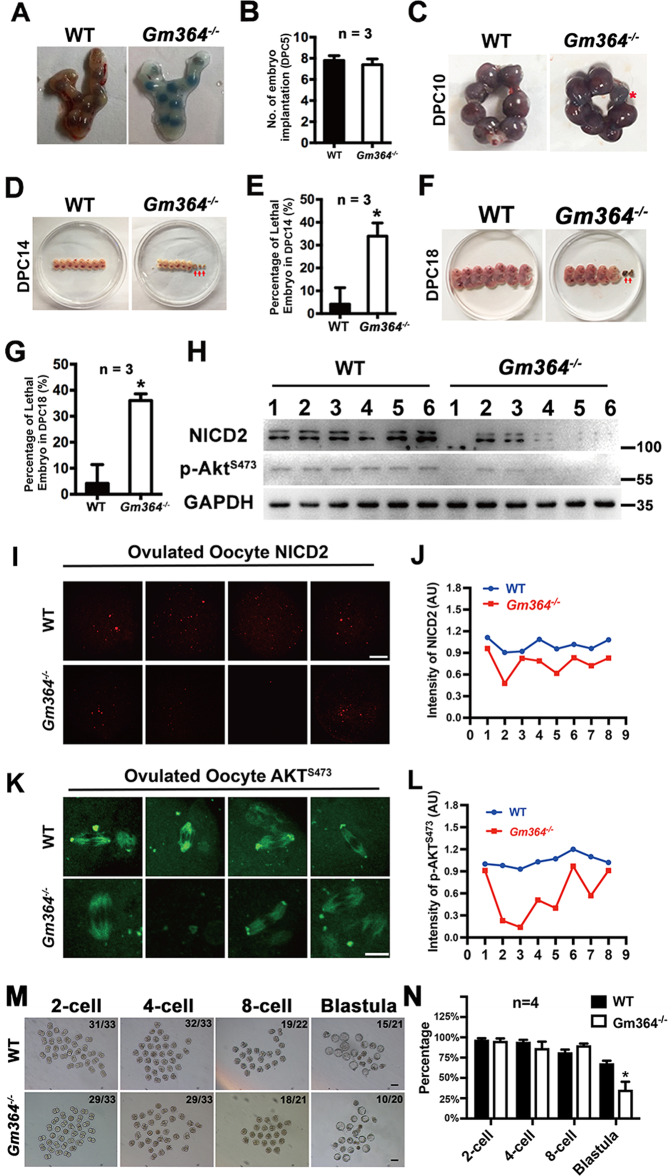
Fig. 7. Gm364 is essential for normal embryo development.
A, B Trypan blue staining and quantification showed that Gm364 knockout did not change the number of implanted embryos at DPC (days post coitum) 5. C At DPC 10, some implanted embryos were abnormally smaller (red asterisk). D–G. Morphological evaluation and quantification showed that, at DPC 14 (D) and (E) or DPC 18 (F) and (G), Gm364 knockout mice had a significantly larger percentage of tiny dead embryos (red arrow) than the WT mice. H Blots showed that, at DPC 21, a large percentage (4 of 6, red arrows) of Gm364-KO mouse embryos had significantly lower NICD2 and p-AKTS473 levels; In contrast, all WT embryos had higher and similar NICD2 and p-AKTS473 levels. J–L Immunofluorescence and quantification showed that NICD2 levels (I) and (J) or p-AKTS473 (K) and (L) are all higher and close to each other in ovulated WT oocytes (blue curves); while lower and very distinct from each other in ovulated Gm364-KO oocytes (red curves). M, N In vitro culture of in vivo fertilized oocytes from 2-cell to blastula showed that the blastula rate of Gm364-KO fertilized oocytes (35.5%) was significantly less than that of WT fertilized oocytes (68.1%). Scale bars for panel (I), 20 μm; scale bars for panel (K), 10 μm; Scale bars for panel (M), 100 μm. *Indicates p < 0.05.