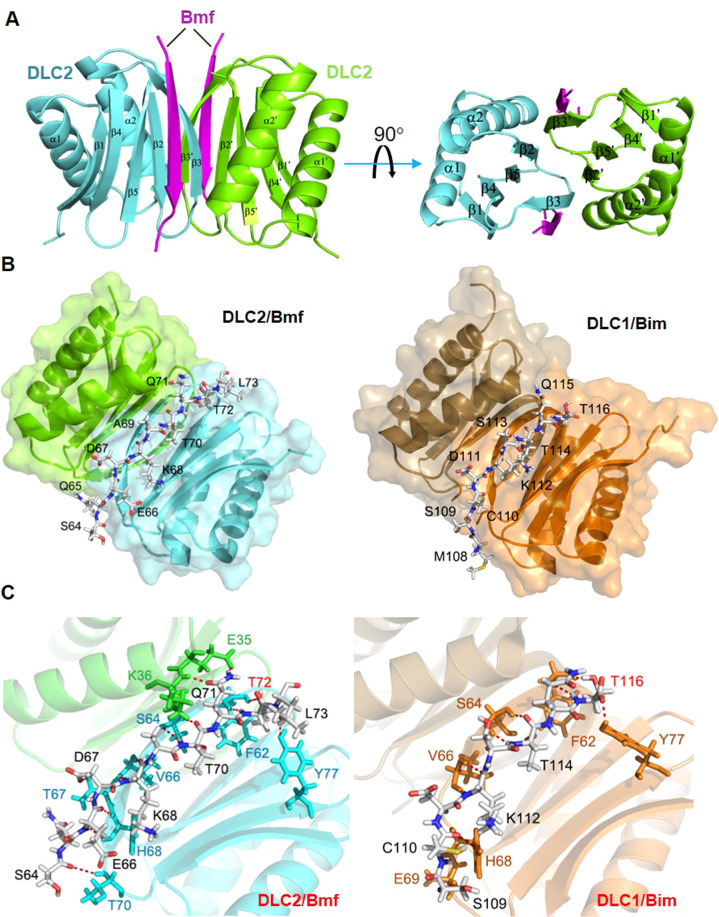
Fig. 5. Structural comparison of the Bmf/DLC2 and Bim/DLC1 complexes.
A Overall crystal structure of the Bmf/DLC2 complex. Two Bmf peptides separately fit into two binding grooves formed by the β1, β3 and β4 strands of one DLC2 monomer and the α2 helix of the partner, at either side of the DLC2 dimer, adopting a dimer/dimer stoichiometry. B Comparison of overall structures between Bmf/DCL2 complex and Bim/DLC1 complex (PDB: 1F95). DLC1 and DLC2 dimers were shown in ribbon diagram (DLC1: orange and brown; DLC2: green and teal) and Bim/Bmf peptides were shown in backbone diagram with each amino acid labeled. Bmf and Bim peptides shared highly similar modes of DLC binding. C Detailed interaction interfaces of Bmf/DLC2 complex (Left) and Bim/DLC1 complex (Right). Bim/Bmf peptides and DLC residues involved in polar contacts were shown in backbone diagram and color labeled. Green and teal: residues from DLC2; Orange: residues from DLC1. T72 (Bmf) and T116 (BimEL) were highlighted in red. Polar contacts were denoted by dashed red lines.