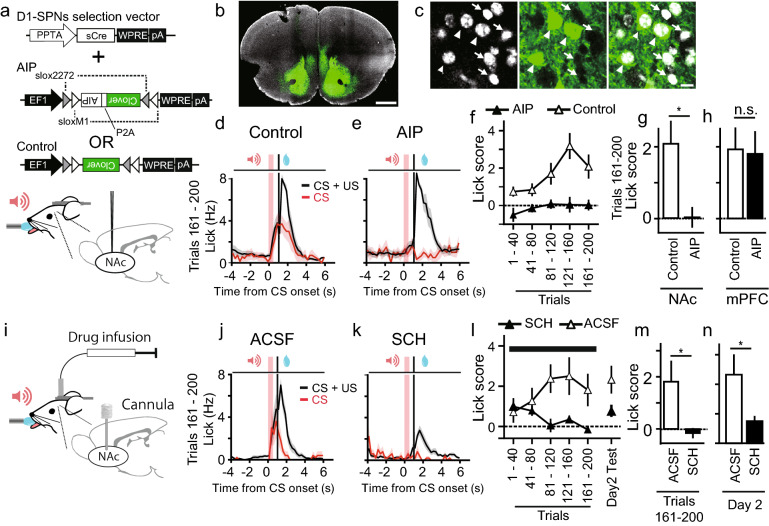
Figure 3.
The effect of a D1 receptor blocker and CaMKII inhibitory peptide (AIP) in the NAc on conditioning. (a) Viral constructs and schematics of injection. (b,c) Confocal images of clover fluorescence (green) and DAPI (white) from a coronal slice, including the NAc. Slices were counter-stained with DAPI, and 35.8% (72/201) of cells were positive for AIP. Arrowheads indicate AIP-positive cells, and arrows indicate negative cells. Scale bars indicate 1 mm (b) and 20 μm (c). (d,e) Averaged PSTHs of the licking responses in CS + US (black) and CS (red) conditionings from mice injected with control (d, n = 7 mice) or AIP (e, n = 6 mice). (f) The peak lick scores are plotted against time for the conditions indicated. (g,h) Average lick scores from eight trials during trials 161–200 from mice with injections in the NAc or injections in the mPFC (this figure, Supplementary Fig. S2 online) were plotted for each condition. *P < 0.05, two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. (i) A schematic diagram for drug infusion into the NAc. (j,k) Averaged PSTHs of the licking responses in trials 161–200 without (j, ACSF, n = 5 mice) or with (k, SCH23390, n = 5 mice) the injection of a D1 blocker during conditioning. (l) The lick scores were plotted against time for the two conditions indicated. Drug infusion was started 30 min before the behavioral experiments and was continued during conditioning as indicated by the black horizontal bar. (m,n) The effect of a dopamine D1 receptor blocker, SCH23390, on conditioning. Averaged lick scores of CS-only trials during trials 161–200 (m) or day 2 (n) were plotted. *P < 0.05, two-sided Mann–Whitney U test, n = 5 mice for SCH23390, n = 5 mice for ACSF.