FIGURE 3.
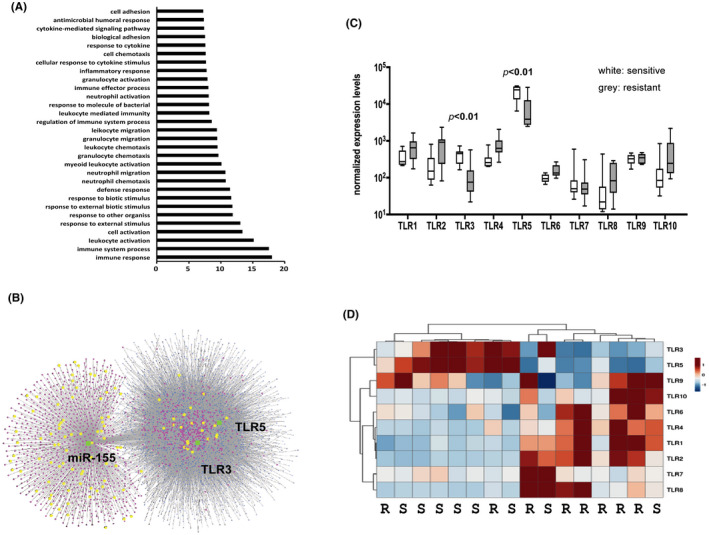
A miR‐155‐related immune network identified Toll‐like receptor 5 as a potential marker for sensitivity to H. pylori eradication therapy. (A) Pathway enrichment analysis linked immune response pathways with responses to H. pylori eradication therapy. Genome‐wide mRNA expression profiles in eight sensitive and eight resistant gastric DSLBCLs identified 563 differentially expressed mRNAs. The online program g:Profiler is used for pathway enrichment analysis on the Gene Ontology (GO) database. The immune response pathway is the most significantly enriched GO pathway. X‐axis: p value for enrichment, adjusted, in –log scale; Y‐axis: significantly enriched pathways, with the most significant one at the bottom. (B) TLR5 and TLR3 in a miR‐155‐centered immune network. An immune network is constructed, using miR‐155 and 563 differentially expressed mRNAs as inputs into the online program miRNet. The constructed network included miR‐155 (green), intermediate miRNAs (blue), 73 non‐differentially expressed mRNAs (red), and 32 differentially expressed mRNAs (yellow). The left cluster is due to mRNAs (red & yellow) regulated by miR‐155 (green) and the right cluster is due to mRNAs (red & yellow) indirectly connected with miR‐155 via intermediate miRNAs (blue). (C) The expression levels of TLRs 1–10 in gastric diffuse large B‐cell lymphomas: TLR5 is a potential predictor of sensitivity to H. pylori eradication therapy. The expression levels of TLRs are extracted from genome‐wide mRNA profiles of eight sensitive and eight resistant cases. The sensitive group had higher expressions of both TLR3 and TLR5 than the resistant group (p < 0.01). Note that the expression level of TLR5 is more than one log higher than all the other TLRs. (D) Hierarchical clustering of gastric diffuse large B‐cell lymphomas with TLRs 1–10. The left sensitive cluster included six sensitive and two resistant cases associated with higher expression levels of TLR3 and TLR5. In contrast, the right resistant cluster included two sensitive and six resistant cases associated with higher expression levels of the remaining eight TLRs. R: resistant and S: sensitive
