Figure 5: Oral oxycodone at behaviorally active doses produces hyperlocomotion and preferentially produces hot plate antinociception compared to tail-flick antinociception.
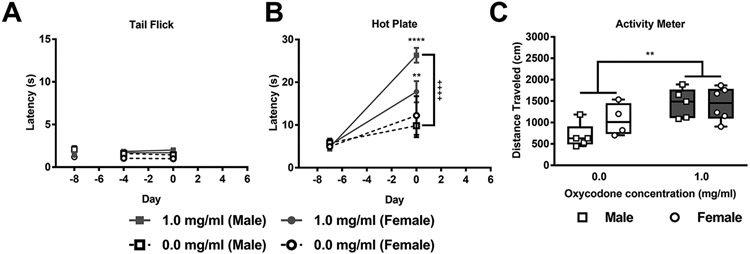
A) Hot water tail-flick latencies showed modest but reliable alterations as a function of the treated bottle and differed by sex. B) Hot plate latencies differed as a function of the treated bottle and session and the interaction between treated bottle and session and sex was significant. Both male and female mice showed longer withdrawal latencies in the hot plate test post-oxycodone compared to their water baseline levels. In male mice, oxycodone consumption increased response latencies in the hot plate test post-oxycodone compared to water consumption. C) Oxycodone consuming mice travelled a greater distance compared to water consuming mice overall in the open field activity meter test. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4-6 per group). “*” indicates high (1 mg/ml) concentration oxycodone group vs. water group where ****p < 0.0001 and **p < 0.01, “+” indicates oxycodone consuming male mice vs. water consuming male mice with the same symbol indications.
