Figure 2.
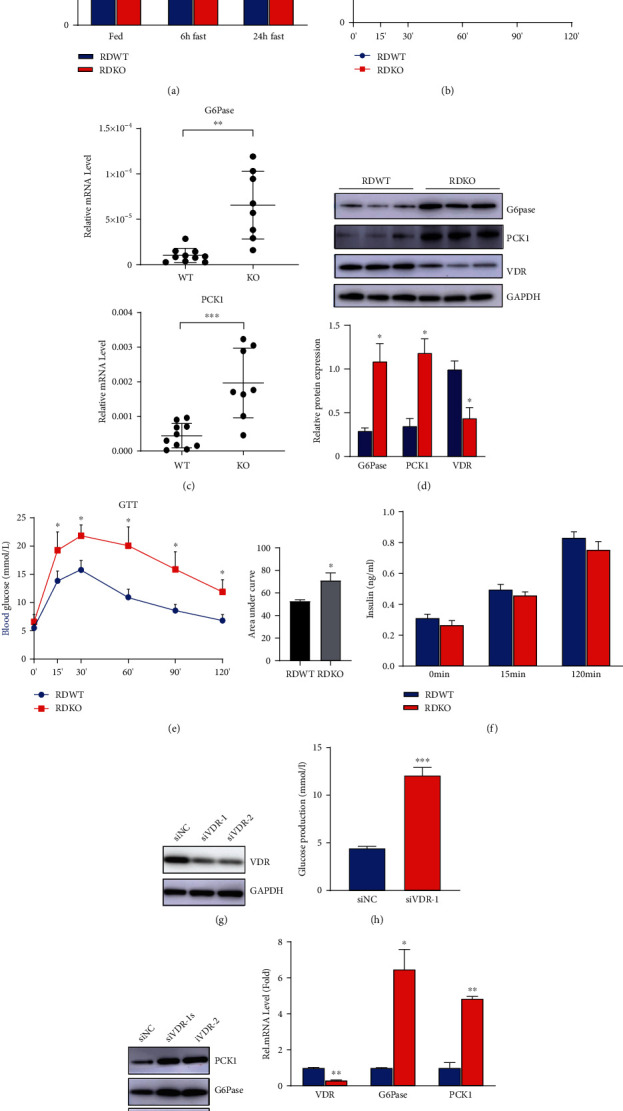
1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency increases hepatic gluconeogenesis. (a) Blood glucose levels of 6-month-old male 1a(OH)ase−/− and wild-type mice with rescued diet at different time points (fasting, fasting for 6 h, fasting for 24 h) (n = 8).∗P < 0.05; blue bar: RDWT group; red bar: RDKO group. (b) PTT was performed in 6-month-old 1α(OH)ase−/− and wild-type mice (n = 8). ∗P < 0.05; blue line: RDWT group; red line: RDKO group. (c) qPCR was used to detect the mRNA expression levels of gluconeogenesis-related genes G6Pase and PCK1 in the liver of 1α(OH)ase−/− mice and wild-type littermates (n = 8). (d) Western blotting was performed to detect the protein expression levels of G6Pase and PCK1 in the liver of the two groups of mice; blue bar: RDWT group; red bar: RDKO group. (e) GTT was performed in 6-month-old 1α(OH)ase−/− and wild-type mice; blue line: RDWT group; red line: RDKO group; n = 8. (f) During the GTT, the serum in two groups of mice was collected at 0, 15, and 120 minutes, and the insulin content in the serum of 1α(OH)ase−/− mice did not show significant difference as compared to the wild-type littermates; blue bar: RDWT group; red bar: RDKO group; n = 8. (g) Western blotting confirmed the siRNA interference efficiency in HepG2 cells. (h) Glucose oxidase method was used to detect the supernatant glucose content of two groups of cells, si-NC group and si-VDR group (n = 3). ∗∗∗P < 0.001. (i, j) Western blotting and qRT-PCR detected the mRNA (j) and protein (i) expressions of G6Pase and PCK1 in the HepG2 cells with VDR knockdown (n = 3). ∗∗P < 0.01; blue bar: RDWT group; red bar: RDKO group; blue line: RDWT group; red line: RDKO group; blue bar: si-NC group; red bar: si-VDR group.
