Figure 1. Effector domain identification, characterization, and function.
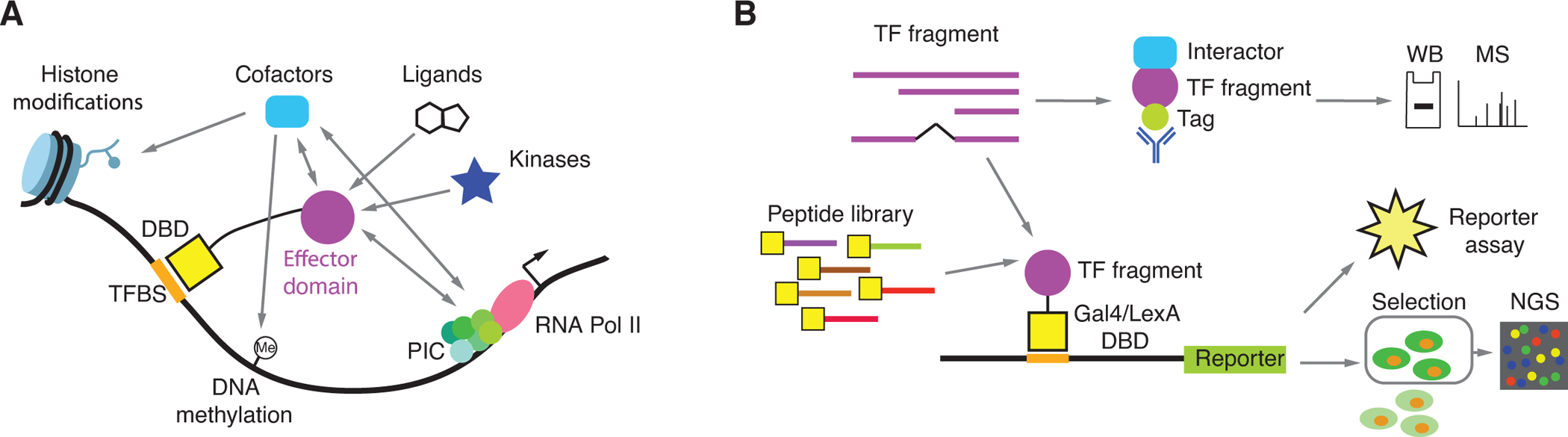
(A) Effector domains can affect gene expression by interacting with cofactors and the preinitiation complex, by directly modifying histone tails, and by leading to changes in DNA methylation states. The activity of some effector domains can be affected by interactions with ligands or by post-translational modifications.
(B) Experimental approaches to identify and characterize effector domains. TF fragments or pool peptide libraries comprised of tilling, random, or mutated peptides are fused to an exogenous DBD (e.g., Gal4, Gcn4, LexA, or rTetR DBDs). Transcriptional activity is often measure using a reporter gene. In the case of high-throughput peptide screens cells with different levels of reporter activity are sorted and the enrichment for sequence coding each peptide is determined by next generation sequencing (NGS).
