Figure 2. Steps of immune recognition and escape.
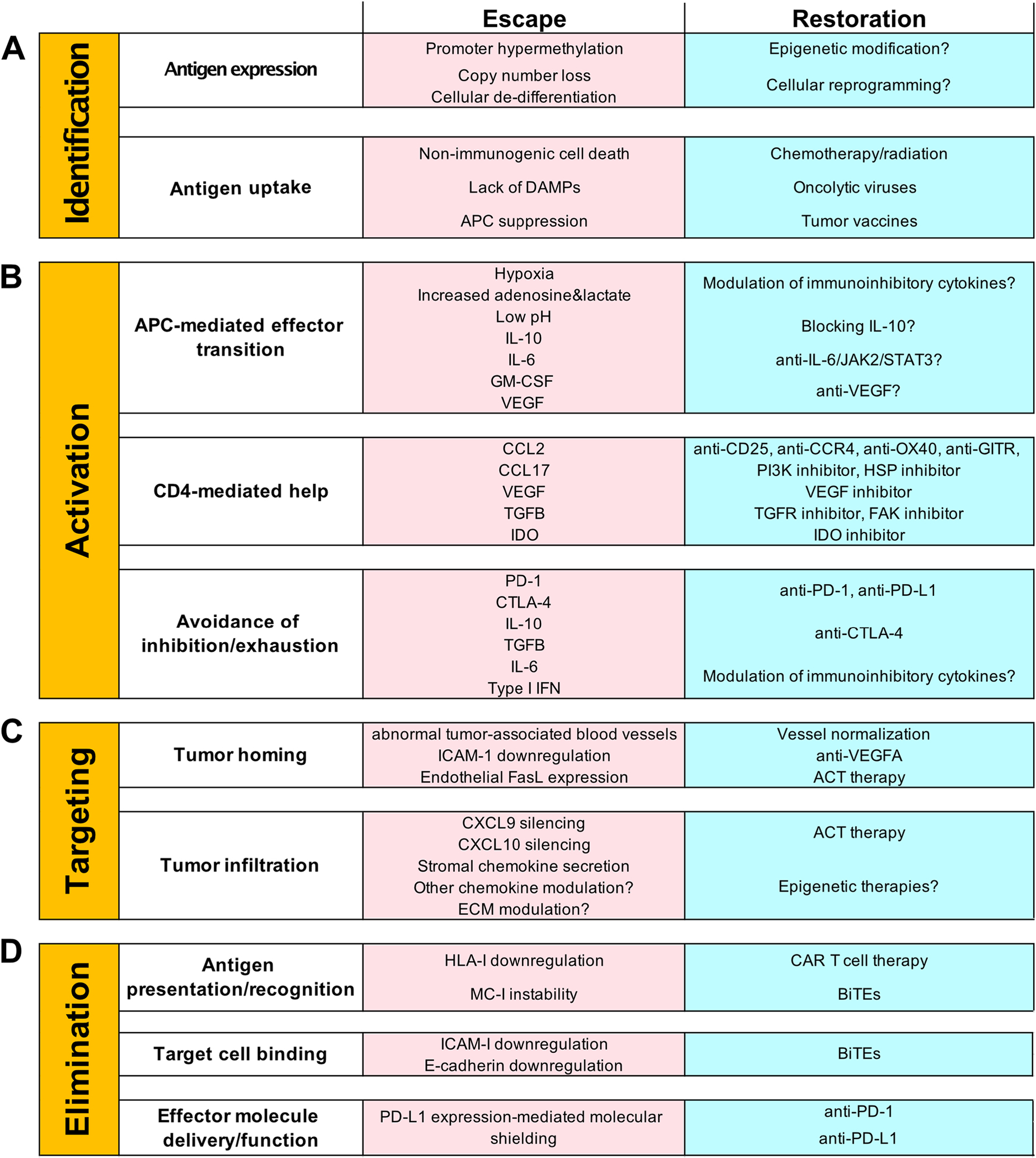
A, Requirements, escape mechanisms, and restoration options of immune identification. The successful identification of malignant cells requires cancer cell antigen expression, followed by antigen uptake by APCs. At each requirement, there is an opportunity for immune escape via the mechanisms listed. Possible methods of therapeutic restoration are shown and therapeutic success would allow for identification to continue. B, Requirements, escape mechanisms and restoration options of activation. Optimal activation of T cells requires an APC-mediated effector state transition, CD4+ T cell-mediated help, and avoidance of inhibition/exhaustion. At each requirement, there is an opportunity for immune escape via the mechanisms listed. Possible methods of therapeutic restoration are shown, and therapeutic success would allow for activation to continue. C, Requirements, escape mechanisms and restoration options of targeting. Successful targeting of immune cells to tumors requires appropriate tumor homing, followed by tumor infiltration. At each requirement, there is an opportunity for immune escape via the mechanisms listed. Possible methods of therapeutic restoration are shown, and therapeutic success would allow for targeting to continue. D, Requirements, escape mechanisms and restoration options of elimination. CTL-mediated cancer cell elimination requires antigen presentation and recognition, target cell binding, and effector molecule delivery and function. At each requirement, there is an opportunity for immune escape via the mechanisms listed. Possible methods of therapeutic restoration are shown, and therapeutic success would allow for elimination to continue.
