Fig. 5.
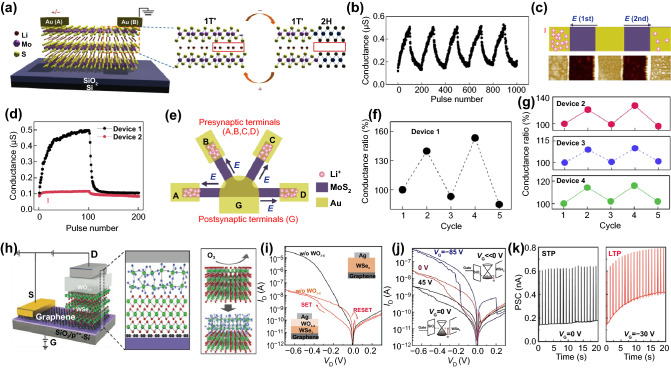
Interactive and regulatory synaptic devices. a Electric field controllable MoS2 devices depending on local 2H–1 T' phase transitions. b Synaptic potentiation and depression by programming pulse. c Schematics of Li+ ions distribution (top), and AFM height images (bottom) and d synaptic potentiation and depression showing synaptic competition. e Schematic of the four electrodes network at the initial condition for synaptic cooperation. f Potentiation and depression in device 1 and g conductance changes of non-stimulated devices 2, 3, and 4 in response to device 1.
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [191]. Copyright 2019, Nature Materials. h Illustration of heterojunction structures composed of WO3–x memristor and WSe2/graphene synaptic barristor. i ID–VD characteristics with (red line) and without a WO3–x layer (black line). j The gate-tunable ID–VD switching curves depending on the Schottky barrier height. k STP to LTP transformation induced by VG change. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [113]. Copyright 2018, Advanced Materials (Color figure online)