Fig. 3.
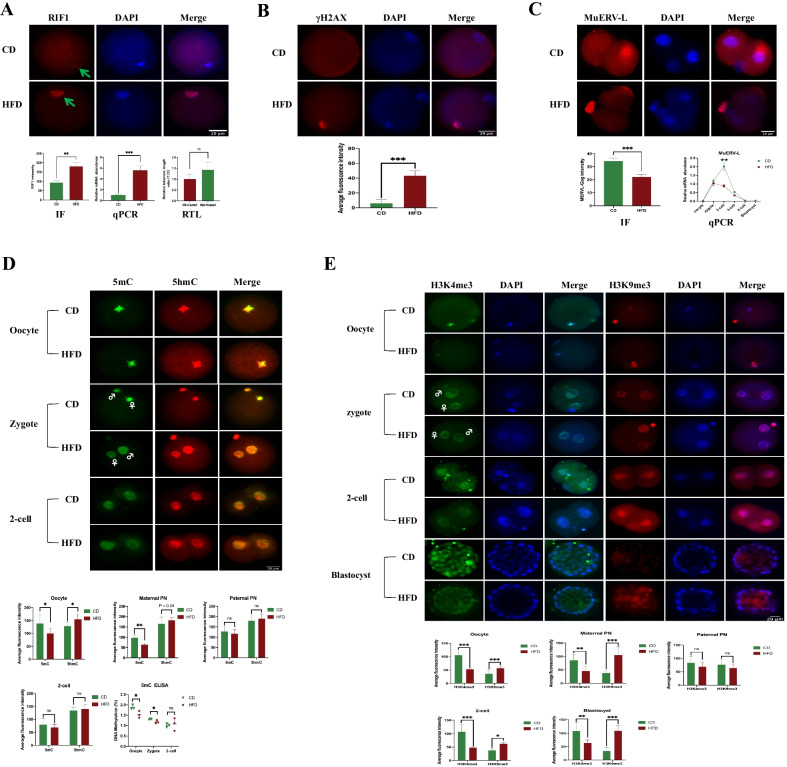
The effects of HFD on RIF1 and epigenetic modification changes in oocytes and preimplantation embryos. A The expression of RIF1 in oocytes of the HFD and CD groups. Top: representative immunofluorescence (IF) images. Arrowheads indicate the expression of RIF1 located in the nucleus. The bar chart in the middle of bottom: qPCR results of RIF1. The bar chart in the lower right corner: qPCR results of the relative telomere length (RTL). B Images of γ-H2AX staining in oocytes of the HFD and CD groups. Bottom: The statistical results are shown. C The expression of MuERV-L gag between the HFD and CD groups. Top: Representative IF images in 2-cell embryos. Since MuERV-L gag could hardly be detected at the other embryonic development stages, only images of 2-cell embryos are presented. Bottom: Statistical results from IF and qPCR. D IF images of 5mC and 5hmC enrichment during ZGA between the HFD and CD groups. The statistical diagrams and the ELISA results of 5mC are shown at the bottom. E IF images of H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 enrichment from oocytes to blastocysts between the HFD and CD groups. The statistical results are shown at the bottom. Throughout, n = 20 in each group for IF analysis, and n = 3 in each group for qPCR analysis. Data are presented as means ± SD. P values are calculated by Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ns indicates not significant. Scale bars are shown in the lower right corner of the captures. HFD high-fat diet, CD control diet. ♀ represents maternal pronuclear (PN). ♂ represents paternal PN