Extended Data Fig. 7. Changes in T cell clones after neoadjuvant treatment and correlation with tumor pathologic regression.
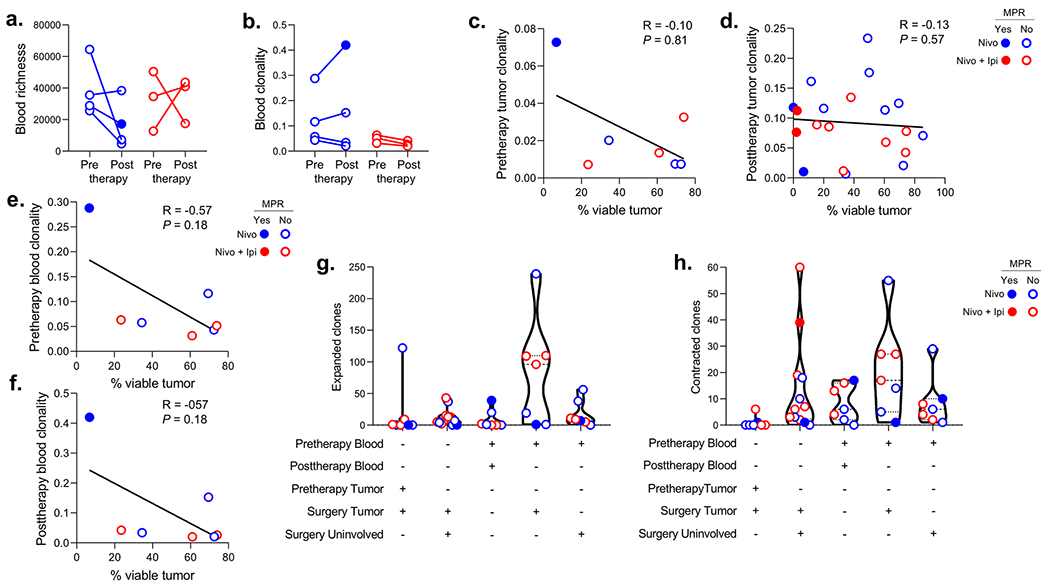
a,b, Changes in TCR repertoire richness (a) and clonality (b) in matched blood samples from pre- to posttherapy (prior to surgery) after neoadjuvant nivolumab (n = 4, blue) or nivolumab plus ipilimumab (n = 3, red). c-f, Correlation between percent viable tumor at surgery and T cell clonality in tumor (c,d) or blood (e,f) pretherapy (c,e) and posttherapy (d,f) with neoadjuvant nivolumab (blue) and nivolumab plus ipilimumab (red). Two-sided P value is from Spearman rank-order correlation. g,h, Number of significantly (two-sided P < 0.01 with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment for false-discovery rate) expanded (g) and contracted (h) T cell clones in matched resected (surgery tumor) vs. pretherapy tumors (n = 7), matched resected tumors (surgery tumor) vs. tumor-adjacent uninvolved lungs (surgery uninvolved) (n = 12), matched posttherapy (prior to surgery) vs. pretherapy blood samples (n = 7), matched resected tumors (surgery tumor) vs. pretherapy blood samples (n = 7) and tumor-adjacent uninvolved lungs (surgery uninvolved) vs. pretherapy blood samples (n = 7) after neoadjuvant nivolumab (blue) and nivolumab plus ipilimumab (red). Data are presented as median with minima, lower and upper quartiles, and maxima. All violin plots show single data points, dashed line shows the median value, dotted lines show lower quartile and upper quartile values of the range; top and bottom of the violin plots indicate the minima and maxima. Closed dots: MPR; Open dots: No MPR.
