Fig. 5. TCR changes in blood and tumors treated with neoadjuvant nivolumab and nivolumab + ipilimumab.
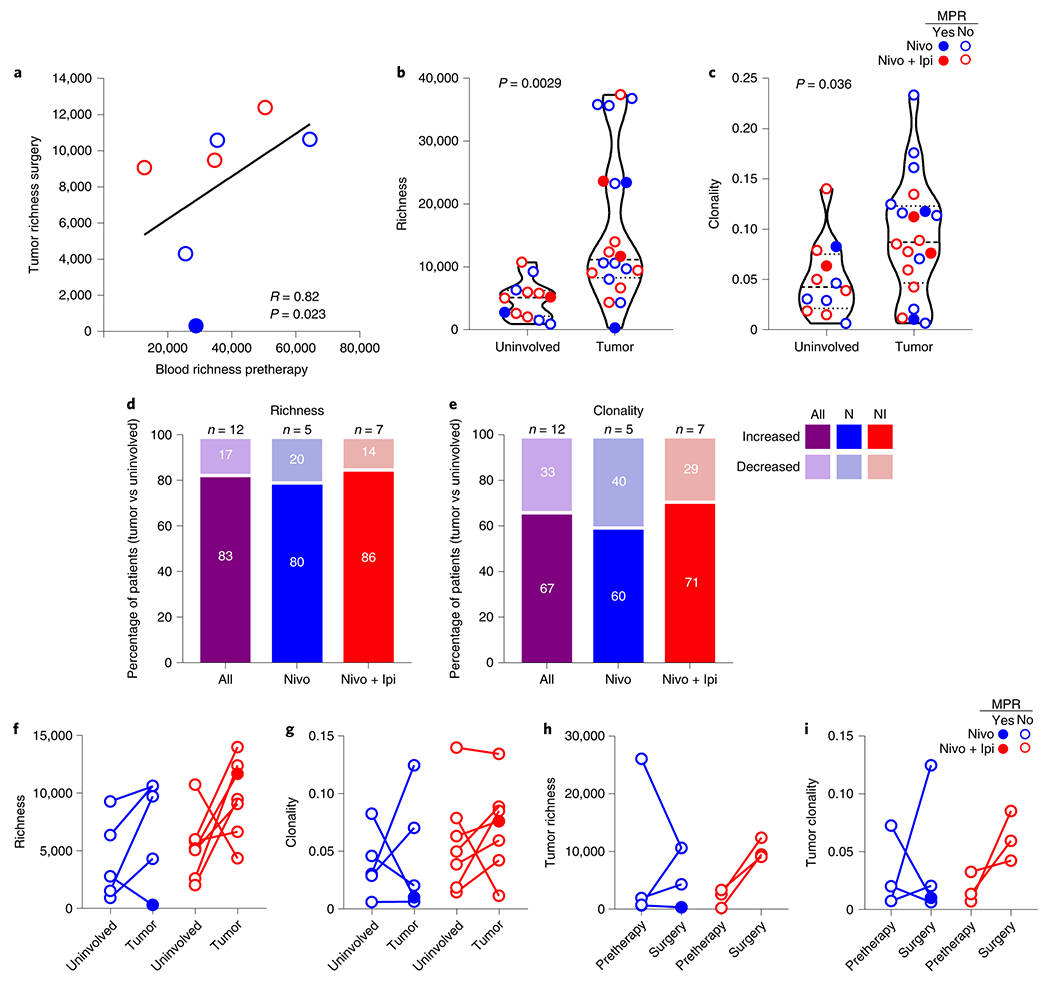
a, Correlation of TCR repertoire richness between the pretherapy (baseline) peripheral blood and resected (surgery) tumors after neoadjuvant nivolumab (n = 4, blue) and nivolumab + ipilimumab (n = 3, red). The two-sided P value is from Spearman’s rank-order correlation. b,c, TCR repertoire richness (b) and clonality (c) between resected tumor-adjacent, uninvolved lungs (n = 12) and resected tumors (n = 20) after neoadjuvant nivolumab (blue) and nivolumab + ipilimumab (red). Data are presented as the median with minima, lower and upper quartiles, and maxima. All violin plots show single data points; the dashed line shows the median value and dotted lines show lower quartile and upper quartile values of the range; the top and bottom of the violin plots indicate the minima and maxima. The two-sided P value is from a two-sample Student’s t-test. d,e, Proportion of patients with increased and decreased TCR repertoire richness (d) and clonality (e) in resected tumors compared with their matched resected, tumor-adjacent, uninvolved lungs (n = 12, purple), after nivolumab (N, n = 5, blue) or nivolumab + ipilimumab (NI, n = 7, red). f,g, Changes in TCR repertoire richness (f) and clonality (g) between matched resected tumors and tumor-adjacent, uninvolved lungs after neoadjuvant nivolumab (n = 5, blue) or nivolumab + ipilimumab (n = 7, red). h,i, Changes in TCR repertoire richness (h) and clonality (i) in matched pretherapy and resected (surgery) tumors after neoadjuvant nivolumab (n = 4, blue) or nivolumab + ipilimumab (n = 3, red). Closed dots: MPR; Open dots: No MPR.
