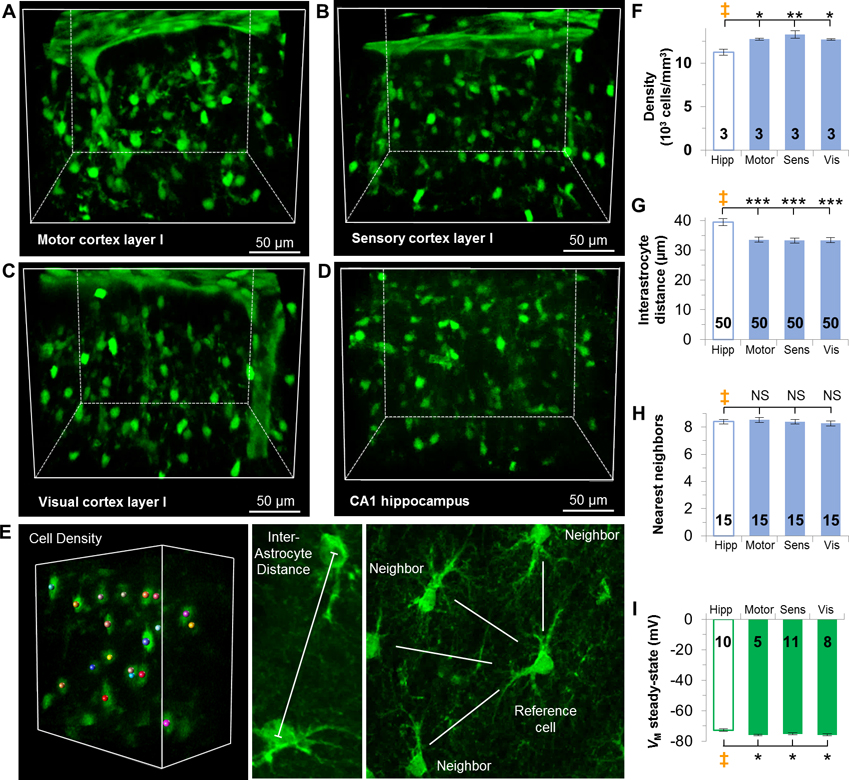
Figure 2. Syncytial isopotentiality occurs in layer I cortical astrocytes across three brain regions.
(A-D) CUBIC optical clearing of brain tissue slices reveals the syncytial organization of astrocytes in layer I of the motor (A), sensory (B), and visual (C) cortices, and CA1 stratum radiatum hippocampal astrocytes (D). E. Representations of astrocyte syncytium anatomical parameters. (F) Astrocyte density is higher in layer I cortices than astrocytes in the hippocampus. (G) The interastrocytic distance was shorter in layer I cortices than the hippocampus. (H) The number of nearest neighbors was comparable between hippocampus and layer I cortices. (I) VM,SS in each layer I cortical area is significantly hyperpolarized than the hippocampus. F, G, H, I: one-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc (‡). *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.01, ***: p < 0.005, NS: p > 0.05.