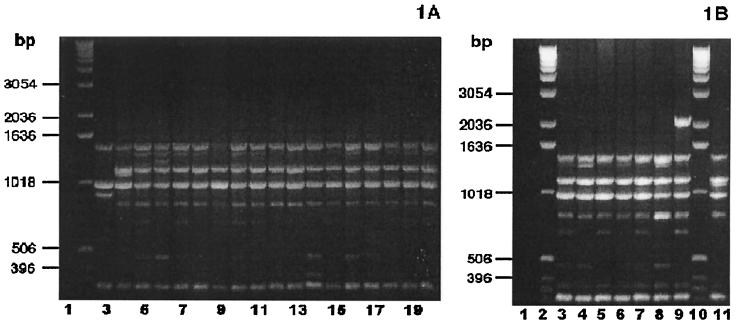
FIG. 1.
P. multocida subsp. septica PCR fingerprint profiles. (A) Thirteen sorbitol-negative, α-Glu-positive and three sorbitol-uncertain, α-Glu-positive P. multocida bite wound isolates, examined by PCR fingerprint analyses using the single primer, M13 core, exhibited the group I PCR fingerprint profile characteristic of P. multocida subsp. septica. (Sorbitol fermentation was based on a consensus of API-20E, PRAS, and Andrades sorbitol fermentation reactions.) Lane 1, negative control (no DNA template); lane 2, DNA ladder; lane 3, P. multocida subsp. multocida ATCC 12947; lane 4, P. multocida subsp. septica ATCC 51688; lanes 5 to 20, bite wound isolates. (B) Seven sorbitol-positive, α-Glu-positive P. multocida bite wound isolates, examined by PCR fingerprint analyses using the single primer, M13 core, showed the group I PCR fingerprint profile characteristic of the P. multocida subsp. septica control strain. Lane 1, negative control (no DNA template); lanes 2 and 10, DNA ladder; lanes 3 to 9, bite wound isolates; lane 11, P. multocida subsp. septica ATCC 51688.