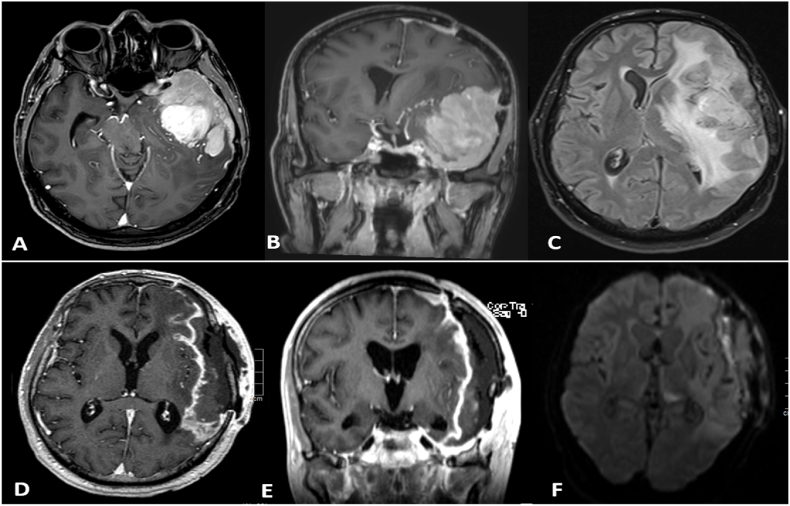
Fig. 4.
Brain MRI with contrast (images A-C) for the first recurrence in 2016: Infiltrative avidly contrast-enhancing extra-axial dural mass at the left frontotemporal convexity with medial extension along the left lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and the lateral wall of the left cavernous sinus. the mass infiltrates the lateral surface of the left frontal and temporal lobes causing vasogenic oedema in the left cerebral hemisphere with resultant mass effect causing rightward midline shift and left uncal herniation.
8 weeks after surgery (images D-F): shows abnormal enhancement in the surgical cavity (D, E) with diffusion restricted subdural fluid collection underneath the craniotomy flap (F), most suggestive of subdural empyema.