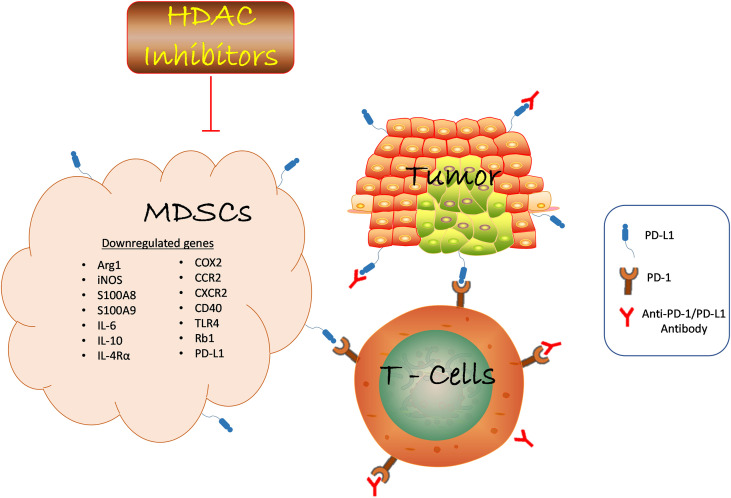
Figure 1.
HDAC inhibition suppresses MDSCs function in the TME and promotes anti-PD-1/PD-L1 tumor immunotherapy. HDAC inhibition blocks tumor-infiltrating MDSCs accumulation in various cancer by downregulating the expression of genes involved in promoting the suppressive role of MDSCs which led to reduced tumor growth. Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody inhibits immune checkpoint proteins expression on tumor and T-cell to confer anti-tumor effect. The combination of HDAC inhibitors and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 promotes T cells activation to inhibit tumor growth. Likewise, HDAC inhibitors augment anti-PD-1/PD-L1 tumor immunotherapy via reduced MDSCs function. Hence, the interaction of several immune cells within the TME determines the success of cancer immunotherapy strategies. HDAC, Histone deacetylase; MDSCs, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; anti-PD-1/PD-L1, antibody against programmed death receptor 1/programmed death-ligand 1; ARG1, arginase 1; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide; IL-6, interleukin 6; IL-10, interleukin 10; IL-4Rα, interleukin 4 receptor alpha; COX2, cyclooxygenase 2; CCR, C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 2; CXCR - CXC chemokine receptor 2; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; Rb1, retinoblastoma 1.