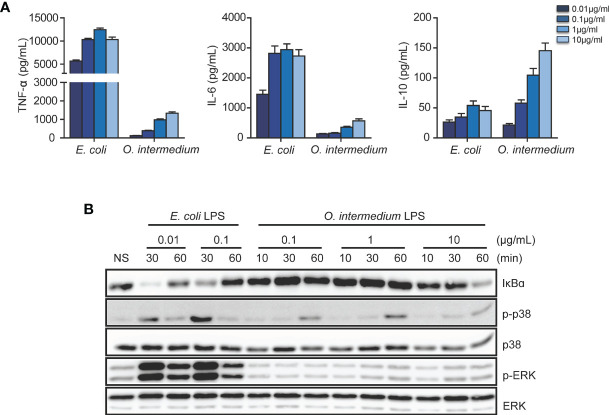
Figure 1.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from O. intermedium induces lower proinflammatory cytokine levels compared to the E. coli LPS. (A) Macrophage cell line J774 was stimulated with O. intermedium LPS or E. coli LPS at a concentration of 0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 µg/ml for 24 h. Cytokine secretion was assayed from macrophage supernatants, and data are expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) Wild-type (WT) peritoneal macrophages were treated with 2 doses of E. coli LPS or 3 distinct doses of O. intermedium LPS for different indicated time points. Nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation was determined by degradation of IκBα and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) [p38 and extracelllular regulated kinase (ERK)] activation by phosphorylation in Western blot. The data are representative of three independent experiments.