Figure 1.
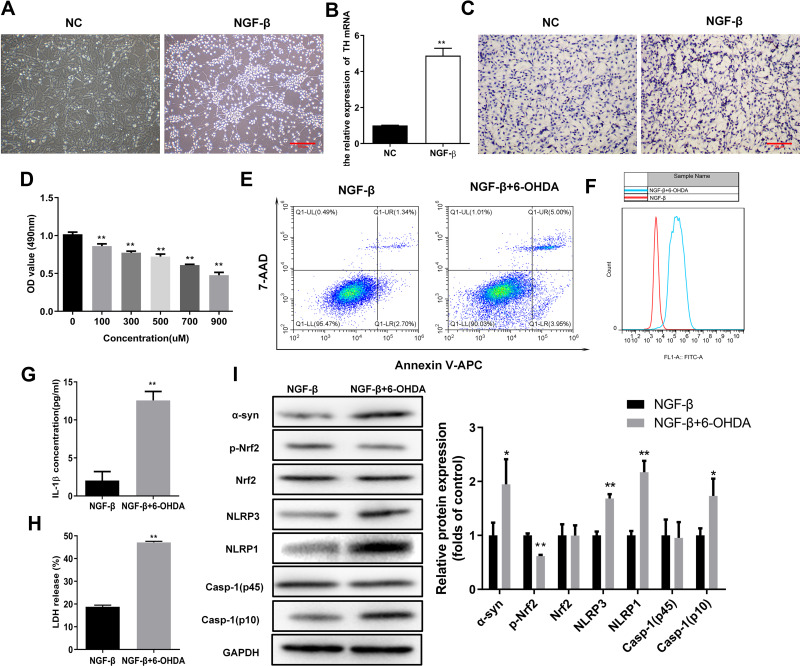
Elevated oxidative stress and pyroptosis in the cellular PD model. (A) Outgrowth of neurites from PC12 cells treated with NGF-β. Morphological alterations of PC12 cells were observed by microscopy following NGF-β treatment for 7 d. (B) Relative TH mRNA levels in PC12 cells treated with NGF-β. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed to detect TH mRNA levels. (C) In situ expression of TH proteins in PC12 cells following NGF-β treatment. TH protein contents in PC12 cells were analyzed by immunocytochemistry. (D) Proliferation of PC12 cells treated with NGF-β and exposed to 6-OHDA (100 μM). Proliferation was assessed by MTS assay. (E) Alteration of apoptosis in PC12 cells following NGF-β induction and 6-OHDA exposure (100 μM). Apoptosis of PC12 cells was evaluated by flow cytometry. (F) Elevated ROS contents in the cellular PD model. Flow cytometry was performed to detect ROS levels in cells. (G and H) Increased IL-1β and LDH release in the cellular PD model. IL-1β (G) and LDH release (H) were detected by ELISA. (I) Alterations of α-synuclein, Nrf2, and pyroptosis marker proteins in the cellular PD model. Protein abundance in cultured PC12 cells was analyzed by Western blot. Relative protein expression was calculated based on the gray values. GAPDH was used as an internal standard. **P < 0.01.
Abbreviations: NC, negative control; NGF-β, nerve growth factor β; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; 6-OHDA, 6-hydroxydopamine hydrobromide; α-Syn, α-synuclein; Nrf2, nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; NLRP1/3, Nod-like receptor protein 1/3; IL-1β, interleukin 1β; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase.