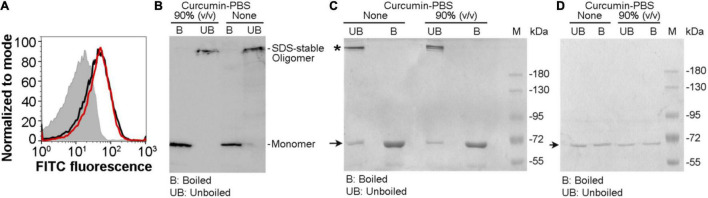
FIGURE 4.
Vibrio cholerae cytolysin retains its ability to bind to the target membranes and forms SDS-stable oligomeric assembly in the presence of the soluble aqueous extract of curcumin. (A) Flow cytometry-based assay showing binding of VCC with human erythrocytes in the presence of the soluble aqueous extract of curcumin in PBS [curcumin-PBS; 80% (v/v)] (red curve). The binding of VCC to the cells in the absence of curcumin extract is shown in black curve. The filled gray curve represents the control cells stained with primary and secondary antibodies, without the VCC treatment. The data shown here is representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) VCC retains its ability to form SDS-stable oligomers in the human erythrocytes membrane ghost in the presence of curcumin-PBS [90% (v/v)]. VCC was incubated with human erythrocytes membrane ghost in the presence or absence of curcumin-PBS, and the membrane-bound VCC was probed by pull down-based assay, followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Sample treated with SDS-PAGE sample buffer without boiling allowed detection of the SDS-stable oligomers formed by VCC. The data shown here is representative of three independent experiments. (C) The ability of VCC to associate and form SDS-stable oligomers in the membrane lipid bilayer of Asolectin-cholesterol liposomes was probed by the pull down-based assay. Liposomes were treated with VCC in the absence or presence of curcumin-PBS [90% (v/v)], and liposome-bound pellet fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining, with or without boiling in the SDS-PAGE sample buffer. Unboiled samples allowed detection of the SDS-stable oligomers formed by VCC. The bands corresponding to the monomeric and oligomeric form of VCC are indicated with arrow and asterisk, respectively. Lane M shows the molecular weight marker. The data shown here is representative of at least three independent experiments. (D) A control experiment was performed to examine whether VCC could form any SDS-stable oligomer in solution in the presence of curcumin extract in PBS, in the absence of the target membranes. VCC (500 nM) was incubated in the absence or presence of the curcumin extract in PBS (90% vol/vol) in a reaction volume of 1 ml in PBS, for 1 h at 25°C. Samples (40 μl) were withdrawn from each reaction mixture, divided into two equal parts, and mixed with SDS-PAGE sample buffer. One part was boiled, while the other part was incubated at room temperature. Unboiled and boiled samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie staining. The bands corresponding to the monomeric form of VCC are indicated with an arrow. Lane M shows the molecular weight marker. The data shown here is representative of three independent experiments. The result showed that VCC did not form any SDS-stable oligomer in solution in the presence of curcumin extract in PBS, in the absence of the target membranes.