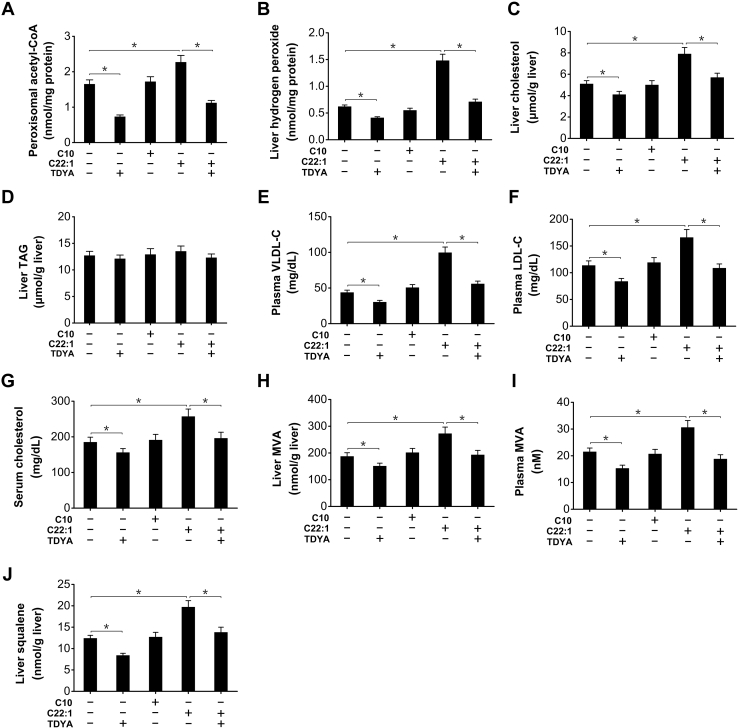
Figure 2.
Increased substrate flux through peroxisomal β-oxidation stimulated biosynthesis of cholesterol in livers of the STZ-induced diabetic mice.A, changes in peroxisomal acetyl-CoA content after treatment of C10, C22:1, and TDYA in the diabetic mice. B, C22:1 treatment significantly increased hydrogen peroxide content in liver of the STZ-induced diabetic mice, which was reduced by pretreatment of TDYA. C, C22:1 treatment increased hepatic cholesterol content in the diabetic mice, as reduced by TDYA. D, C22:1 treatment showed no significant increase in liver TAG in the diabetic mice. E–G, C22:1 treatment significantly elevated plasma levels of VLDL-C (E), LDL-C (F), and serum cholesterol (G) in the STZ-induced diabetic mice, as abolished by pretreatment with TDYA. H and I, C22:1 treatment significantly increased liver (H) and plasma (I) MVA level, as reduced by pretreatment with TDYA. J, C22:1 treatment significantly increased liver squalene content in the diabetic mice, as reduced by TDYA. Mean ± SEM, n = 8, ∗p < 0.05 by t test between paired conditions. LDL-C, low density lipoprotein-cholesterol; MVA, mevalonic acid; STZ, streptozotocin; TAG, triacylglycerol; TDYA, 10,12-tricosadiynoic acid; VLDL-C, very low density lipoprotein-cholesterol.