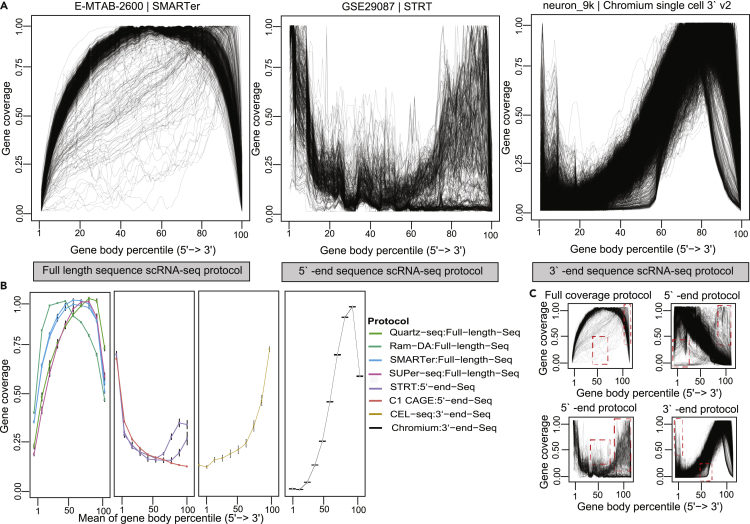
Figure 1.
scRNA-seq gene body coverage skewness and skewness distribution
Three scRNA-seq datasets.
(A) Distribution of mapped reads (tags) across genes. Each panel shows the gene body coverage percentile per dataset. The x axis represents the gene body from 5′ end to 3′ end scaled from 0 to 100, and the y axis denotes gene coverage (0–1). lThe plot of the dataset (ArrayExpress: E-MTAB-2600) generated by SMARTer protocol (full-length sequence) contains cells with low coverage in the middle of the gene region and cells with high coverage in the 3′ -end of the gene region. Although the dataset (NCBI GEO:GSE29087) generated by STRT (5′ -end sequence) contains cells with high coverage both in the middle and the 3′ -end region of the gene. The third dataset from 10x Genomics generated by single-cell 3′ -end protocol contains cells with high coverage in the 5′ -end region of the gene and cells with low coverage in the middle of the gene.
(B) Mean of the gene body coverage for different scRNA-seq methods. Error bars represents the standard error of the mean (SEM).
(C) Skewness and bias in gene body coverage for cells highlighted with a red dashed box.