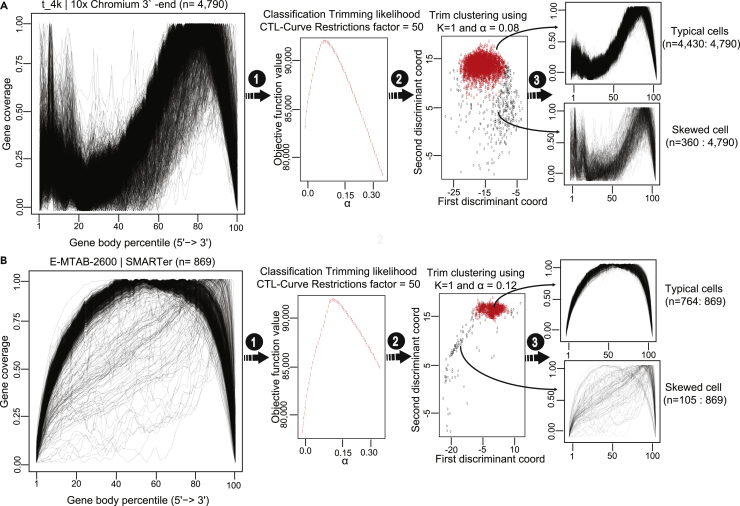
Figure 3.
Classification of the typical and skewed coverage distribution cells
(A and B) Application of SkewC in two different datasets. The gene body coverage matrix is computed and visualized left chart, (1) the gene body coverage matrix used as input to compute the optimum alpha value. The middle chart shows the CTL-curve with optimal alpha value. (2) The selected alpha value used as input for trim clustering on the coverage matrix. A proportion of the most outlying observations is trimmed (the skewed cells). (3) This resulted in two sets of cells: typical cells (with normal gene coverage) and skewed cells (with skewed coverage distribution).