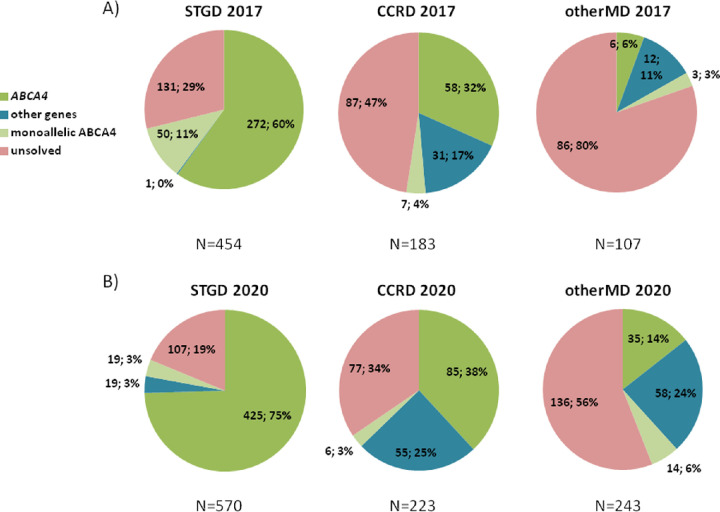
Figure 1.
Diagnostic yields of patients with Stargardt, cone and cone-rod dystrophies, and other maculopathies regarding their genotype. (A) Before exome sequencing and screening of ABCA4 introns. A total of 744 patients were recruited until January 2017. STGD diagnosis patients presented biallelic mutations in the ABCA4 gene in 272 of the 454 cases (60%), and only one patient was characterized with mutations in other gene, PRPH2. The remaining patients were uncharacterized, with 50 (11%) of them carrying one pathogenic allele in the ABCA4 gene. This gene also explained one-third (58/183) and 5.7% (6/107) of the characterized CCRD patients and otherMD patients, respectively. Pathogenic variants in other genes were identified in 17% (31/183) and 11% (12/107) of CCRD and otherMD cases, respectively. Finally, 364 patients remained unsolved, including 60 that were monoallelic for ABCA4. (B) After exome sequencing and screening of ABCA4 introns. A total of 1036 ar/sMD cases were studied or restudied by the end of this study, October 2020. Three quarters of STGD patients (425/570) were characterized with biallelic ABCA4 mutations, 3% (19/570) presented a single pathogenic variant in this gene, and 3% (19/570) presented mutations in other IRD genes. The 19% (107/570) of studied patients remained genetically unsolved. Among the CCRD cases, a 38% (85/223) were found to carry mutations in ABCA4, and one-quarter (55/223) presented mutations in other IRD genes. In the case of otherMD patients, 14% (35/243) presented biallelic ABCA4 pathogenic variants, whereas 24% (58/243) carried mutations in other genes. CCRD and otherMD unsolved cases, including monoallelic ABCA4 patients, were 37% (83/223) and 62% (150/243) respectively. N, total of patients.