FIGURE 10.
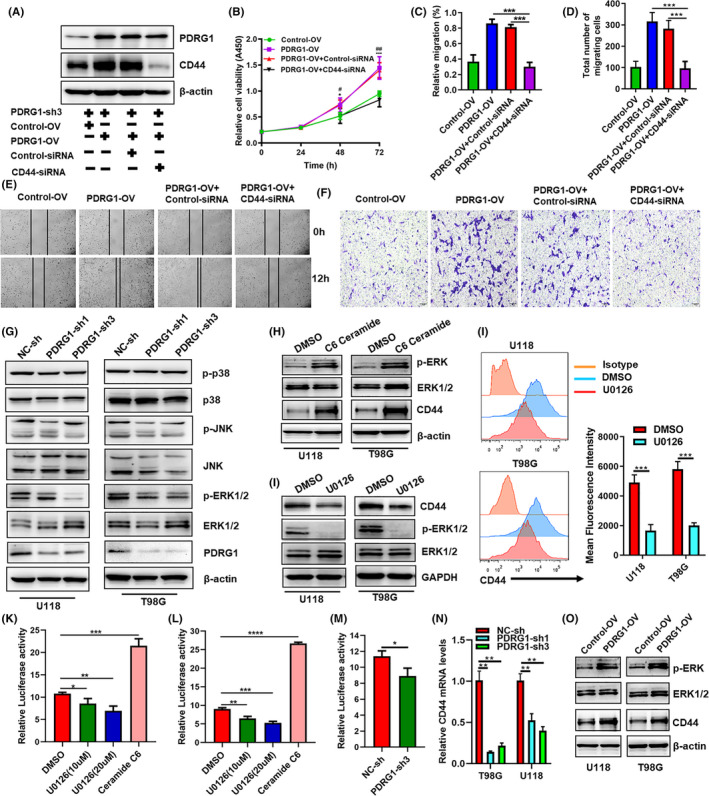
PDRG1 promotes the proliferation and migration of GBM cells by the MEK/ERK/CD44 pathway. A, The PDRG1 stable knockdown U118 cells were transfected with either PDRG1 overexpression lentivirus (PDRG1‐OV) or control lentivirus (Control‐OV). The expression of CD44 was knocked down by siRNA (CD44‐siRNA) silencing. Negative control (Control‐siRNA) was used. Immunoblot assay analyzed the PDRG1and CD44 protein levels. B, The viability of U118 treated as indicated was assessed in 72 hours after seeding. Control‐OV vs PDRG1‐OV (*P < 0.05, ***P <0.001), PDRG1‐OV+Control‐siRNA vs PDRG1‐OV+CD44‐siRNA (#P <0.05, ##P <0.01). The migration ability of U118 and T98G cells treated as indicated was assessed by wound healing assay (C, E) and Transwell assay (D, F). (G) Western blot analysis of the level of p‐ERK1/2, ERK1/2, JNK, P38, p‐P38 and p‐JNK in U118 and T98G cells. (H, I) Cells were treated with MEK inhibitor U0126 or ERK activator C6 ceramide. Western blot analysis of the level of p‐ERK1/2, ERK1/2, and CD44 in U118 and T98G cells. (J) The surface expression of CD44 was measured by flow cytometry. The cells were co‐transfected with indicated CD44 promoter‐luciferase and Renilla plasmids in triplicate. The wildtype 293T (K) and U118 (L) were treated with U0126 or C6 ceramide, and CD44 luciferase activity was evaluated. Luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla activity to control. M, The PDRG1 stable knockdown U118 were transfected with CD44 promoter‐luciferase and Renilla plasmids, CD44 luciferase activity was evaluated. N, q‐PCR analysis of the mRNA level of CD44 in PDRG1 stable knockdown cells. O, Western blot analysis of the level of p‐ERK1/2, ERK1/2, and CD44 in PDRG1 rescued U118 and T98G cells. Data represent one of three independent experiments. Error bars, SD
