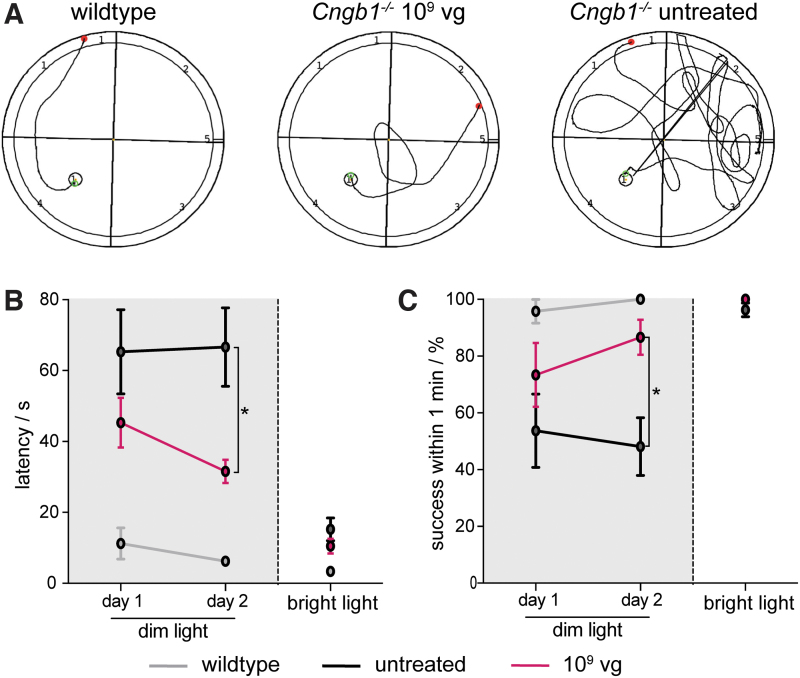
Figure 4.
rAAV5.hCNGB1 results in improved spatial navigation of treated Cngb1−/− mice under dim light conditions. (A) Representative swimming tracks of 9-month-old wild-type (n = 4), untreated (n = 9) and mid-dose–treated (treated at 4 weeks with 109 vg of rAAV5.hCNGB1; n = 5) Cngb1−/− mice in a visual water maze task under dim light conditions. (B) Quantification of latency time until a visible swimming platform was reached during two dim light and one bright light testing days. In contrast to untreated Cngb1−/− mice, those treated with rAAV5.hCNGB1 could improve their performance from days 1 to 2 and needed a shorter time to find the platform on the second test day. (C) Quantification of the success score to locate the swimming visible platform within 1 min (percentage of total runs). Untreated Cngb1−/− mice had a chance success rate of ∼50% on both dim light test days. Again, treated Cngb1−/− mice could improve their performance on reaching a success rate of >80% on day 2. (B, C) Mice from all test groups performed well on the third test day under bright light confirming sufficient remaining cone-mediated vision functionality in the untreated Cngb1−/− mice. Values are given as mean ± SEM (unpaired two-way ANOVA with Sidak's post hoc test; *p ≤ 0.05). Color images are available online.