Figure 2.
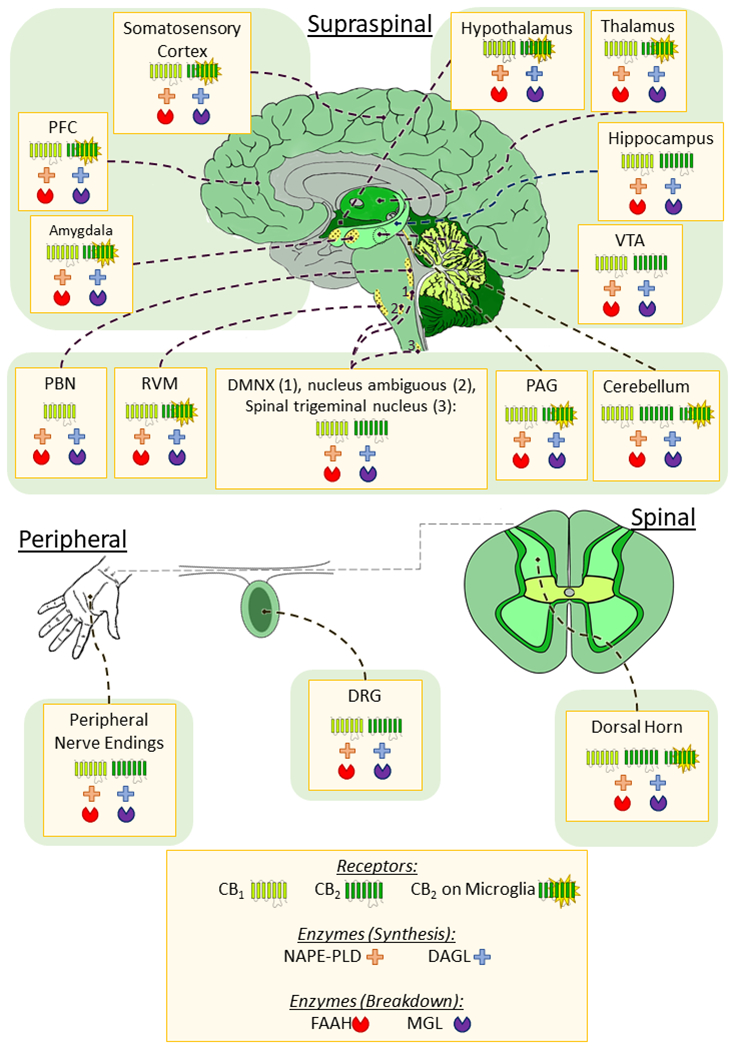
Distribution of the cannabinoid receptors and enzymes associated with endocannabinoid synthesis and degradation in pain pathways. The endcannabinoid system is widely distributed throughout regions associated with pain processing and modulation in the brain, spinal cord and periphery; Most particularly the CB1 receptor and the enzymes responsible for endocannabinoid synthesis (NAPE-PLD, DAGL) and degradation (FAAH, MGL). CB2 receptors are less abundant in the brain and are primarily located on microglia, however studies have shown expression of CB2 on neurons in the VTA, and several discrete nuclei of the brainstem. CB1 is also expressed on microglia at a lower level than CB2, and effects of CB1 on microglia may be mediated by neuronal CB1. Therefore, this was not depicted above. In the DRG and periphery both CB1 and CB2 receptors can be found on neurons (and glia in the dorsal horn), as well as the endocannabinoid enzymes. PFC – prefrontal cortex; VTA – Ventral Tegmental Area; PAG – periaqueductal grey; RVM – rostral ventromedial medulla; PBN – parabrachial nucleus; DMNX - dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve; DRG – dorsal root ganglion; CB – cannabinoid receptor; NAPE-PLD – N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase D; DAGL – diacylglycerol lipase; FAAH – fatty acid amide hydrolase; MGL – monoacylglycerol lipase.
